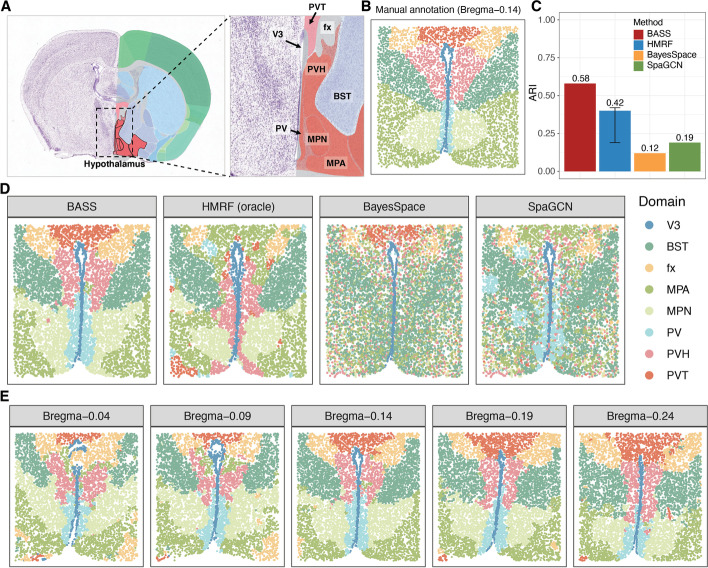
Fig. 6.
Detecting spatial domains in the MERFISH dataset. A An anatomic reference atlas obtained from the Allen Mouse Brain Atlas displays the spatial domains of the mouse hypothalamus region. B Annotated spatial domain labels for the tissue section Bregma-0.14 based on spatial gene expression patterns and the Allen Mouse Brain Atlas. C Barplots of ARI show the accuracy of different methods for spatial domain detection on the tissue section Bregma-0.14. The compared methods include BASS, HMRF, BayesSpace, and SpaGCN. For HMRF, the range of ARI based on a pre-defined list of βs is shown with an error bar. D The identified spatial domains on the tissue section Bregma-0.14 are shown for BASS, HMRF, BayesSpace, and SpaGCN. E The identified spatial domains on five tissue sections (Bregma-0.04, Bregma-0.09, Bregma-0.14, Bregma-0.19, and Bregma-0.24) were obtained with the multi-sample analysis of BASS. V3: the third ventricle; BST: bed nuclei of the strata terminalis; fx: columns of the fornix; MPA: medial preoptic area; MPN: medial preoptic nucleus; PV: periventricular hypothalamic nucleus; PVH: paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus; and PVT: paraventricular nucleus of the thalamus