Fig. 5.
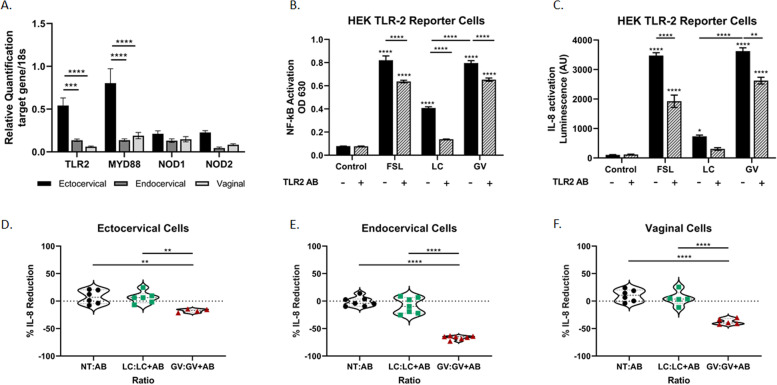
Blocking the TLR2 receptor significantly reduces L. crispatus and G. vaginalis-induced NF-κB and IL-8 activation. TLR2, MYD88, NOD1, and NOD2 are expressed in cervicovaginal epithelial cells, but expression varies by epithelial cell type (A). Blocking the TLR2 receptor in the HEK TLR2 reporter cells significantly reduced L. crispatus and G. vaginalis-induced NF-κB activation (B) and only G. vaginalis-induced IL-8 (C). The TLR2 agonist FSL was included as a positive control. Blocking the TLR2 receptor in cervicovaginal epithelial cells resulted in a reduction in G. vaginalis-induced IL-8, but no effect was seen in L. crispatus treated cells (D, E, F). Data is expressed as a percent reduction of the ratio of treatment alone to treatment plus anti-TLR antibody (A, B). Values are mean ± SEM. Asterisks over the individual bars represent comparisons to control; asterisks over solid lines represent comparisons between treatment groups. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001