Figure 1. Overview of conformational anti-amyloid antibody isolation from yeast-displayed libraries.
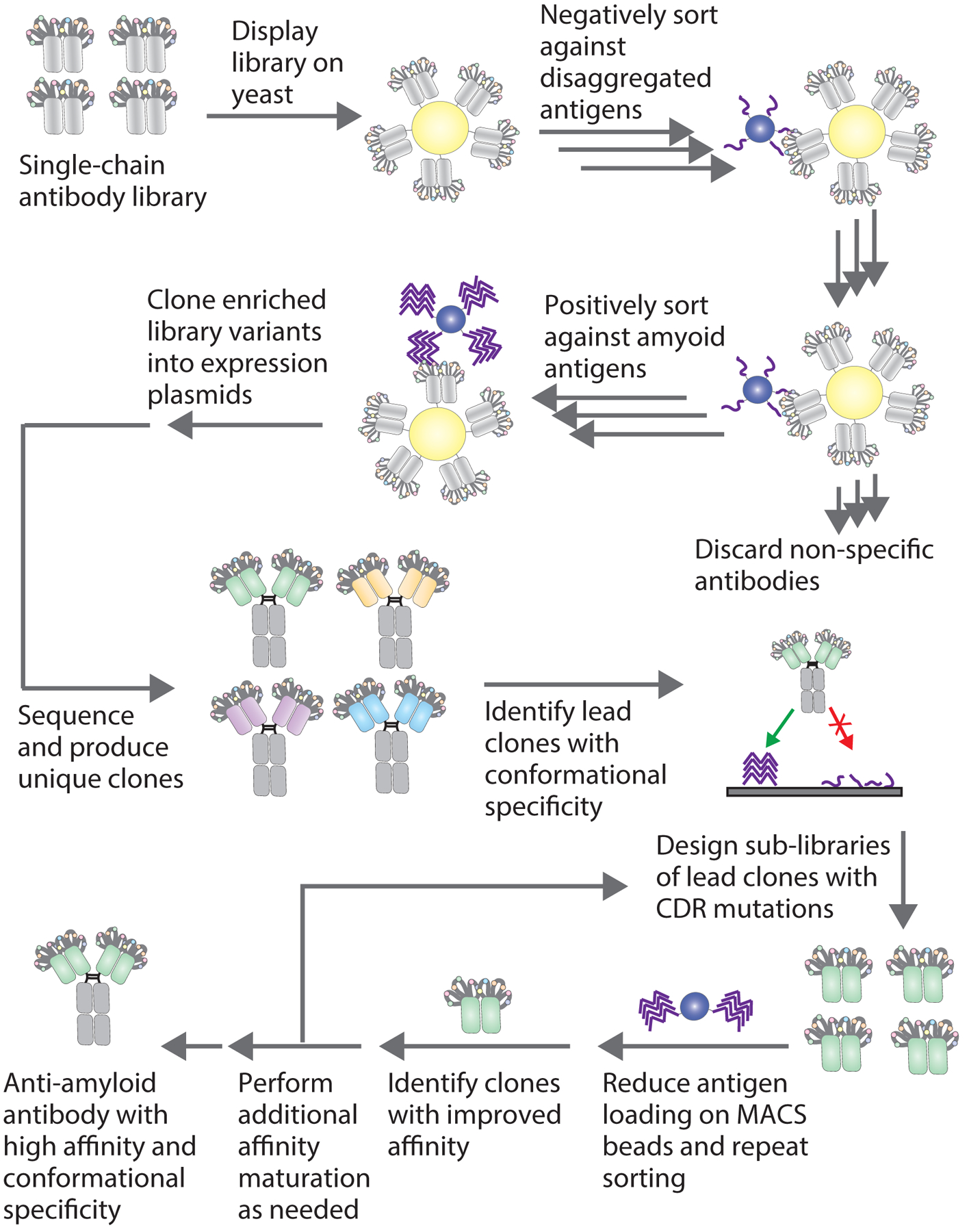
Single-chain antibody libraries displayed on yeast are sorted negatively to remove clones which bind to disaggregated antigen and positively to enrich clones which bind to amyloid aggregates. Negative selections can be performed using either magnetic-activated cell sorting (MACS) or fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS), and positive selections are performed with amyloid aggregates immobilized on beads using MACS. After several rounds of enrichment, the selected antibodies are cloned directly into Fc-fusion plasmids and expressed in mammalian cells. Individual antibody clones are analyzed using flow cytometry for affinity to amyloid fibrils and conformational binding to fibrils in the presence of disaggregated antigen. Clones identified with affinity and conformational specificity for the target amyloid fibrils are then affinity-matured through the preparation of yeast surface displayed sub-libraries. Sub-libraries are sorted stringently by reducing antigen loading or the number of antigen-coated beads to select for clones with improved affinity and conformational specificity.
