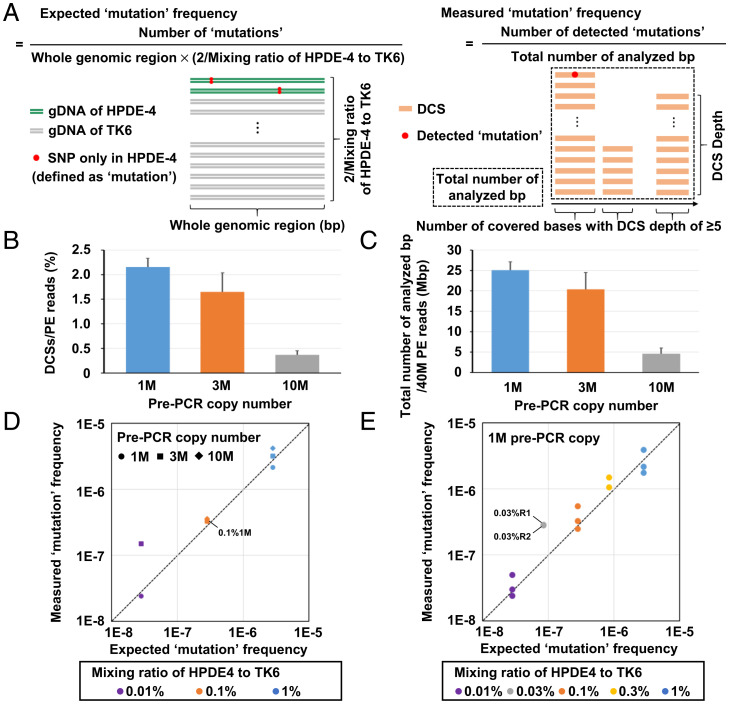
Fig. 2.
Detection of artificially prepared rare mutations. (A) Schema of expected and measured mutation frequencies using model DNA samples. A small amount of HPDE-4 gDNA was mixed into TK6 gDNA, and SNPs present only in HPDE-4 were defined as mutations (artificially prepared mutations). (B) Efficiency in DCS creation. The percentage of DCSs created from PE reads using three pre-PCR copy numbers (1 M, 3 M, and 10 M; n = 3) was analyzed. 1 M pre-PCR copy number showed the highest efficiency to create DCSs. Error bar represents the SD. (C) Total number of analyzed base pairs from 40 M PE reads by EcoSeq. Total number of analyzed base pairs from 40 M PE reads using three pre-PCR copy numbers (1 M, 3 M, and 10 M; n = 3) was compared. 1 M pre-PCR copy number allowed the largest total number of analyzed base pairs. Error bar represents the SD. (D) Accordance between the measured and expected mutation frequencies. The libraries with three mixing ratios (1, 0.1, and 0.01%) prepared from three pre-PCR copy numbers (1 M, 3 M, and 10 M) were analyzed. High accordance was shown in all three mixing ratios prepared from 1 M pre-PCR copy number. No mutations were detected with a mixing ratio of 0.01% and 10 M pre-PCR copy number. (E) Accordance with two additional mixing ratios. The libraries with five mixing ratios (1, 0.3, 0.1, 0.03, and 0.01%) prepared from optimal pre-PCR copy number (1 M) were analyzed in triplicates (1, 0.1, and 0.01%) or duplicates (0.3 and 0.03%). High accordance was shown in all five mixing ratios.