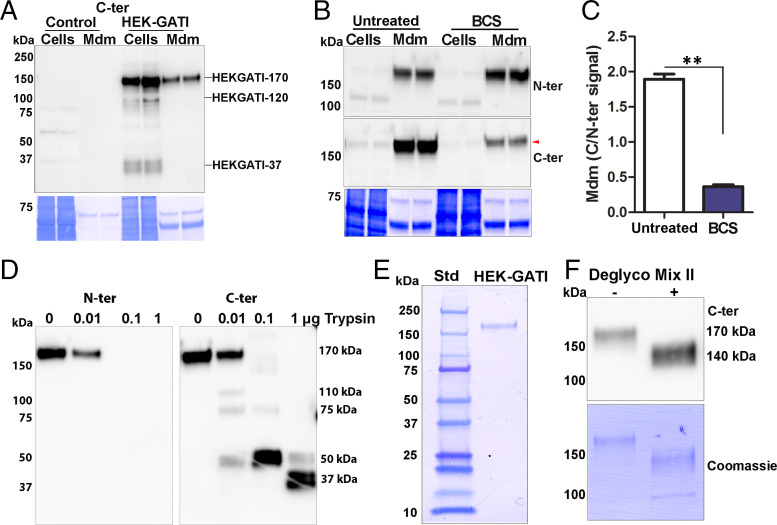
Fig. 4.
HEK cell proGATI contains a stable, amidated C-ter domain. (A) Immunoblot of cell extracts (Cells) and medium (Mdm) prepared from nontransfected cells (Control) and HEK-GATI cells; 20 μg cell extract protein (∼10% of total) and ∼1% of the medium collected over an 18 h time period were analyzed using affinity-purified C-ter antibody. A 170-kDa protein (HEK-proGATI) was detected in both cells and spent medium while 120-kDa and 37-kDa bands containing the amidated C terminus were detected only in cells. (B) Analysis of C-terminal amidation of full-length 170-kDa HEK-proGATI. Medium (Mdm; 5% of total) and cell lysates (Cells; 15 µg, ∼20% of total) from Untreated and BCS-treated cells grown in serum-free media were analyzed. The C-ter signal for HEK-proGATI in the medium was reduced following BCS treatment (red arrowhead), whereas the N-ter signal was unaffected. (C) The C-ter/N-ter signal ratio for HEK-GATI-170 was reduced following BCS treatment. Results are the average of duplicates; **P < 0.001. (D) Medium collected from HEK-proGATI cells was digested by addition of trypsin (10 µL medium plus indicated amount of trypsin); samples were fractionated by SDS/PAGE and probed with C-ter antibody, which detected the indicated cleavage products. The N-ter antibody epitope contains a Lys residue, and is destroyed by trypsin treatment. The results were replicated in independent experiments. (E) SDS/PAGE of purified HEK-proGATI (SI Appendix, Fig. S5C); Coomassie-stained PVDF membrane is shown. (F) Digestion of purified HEK-proGATI with protein deglycosylation Mix II reduced its apparent molecular mass by ∼30 kDa.