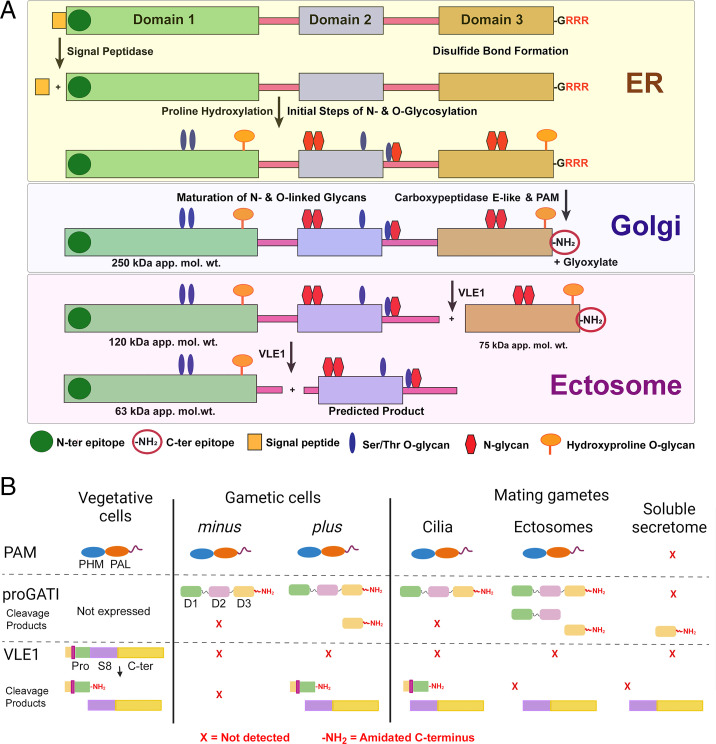
Fig. 8.
ProGATI processing pathway. (A) Diagram illustrating the processing pathway of preproGATI that occurs as it traffics through the ER and Golgi and subsequently enters cilia and ectosomes. The signal peptide (orange box) is removed in the ER by signal peptidase. Addition of N-linked sugars (red) begins in the ER, as does modification of Pro to HyP by prolyl hydroxylases. As proGATI moves into the Golgi complex, more complex sugars and O-linked sugars on HyP (orange) and Ser/Thr (blue) residues are added, leading to the higher apparent molecular mass (∼250 kDa) of proGATI. A carboxypeptidase sequentially removes the C-terminal Arg residues and generates a Gly-extended substrate for PAM. PAM converts this into the amidated product proGATI-amide (indicated by -NH2) in a two-step reaction, and releases glyoxylate as a byproduct. This 250-kDa amidated proGATI then moves to the ciliary membrane. Once on cilia, or as it moves from cilia into nascent ectosomes, 250-kDa proGATI is cleaved by VLE1 producing the 120-kDa N-terminal and amidated 75-kDa C-terminal fragments. Cleavage of the 120-kDa product at a second putative prohormone convertase site located in the linker between domains 1 and 2, or at a dibasic site at the C-terminal end of domain 1, might produce the 63-kDa N-terminal fragment and a second product containing domain 2 for which no probe currently exists. (B) Diagram illustrating the presence and absence of PAM, amidated full-length proGATI (indicated by -NH2) and its various fragments, and the cleaved/amidated subtilisin-like endoprotease VLE1 in cilia of minus and plus vegetative and gametic cells, and in ectosomes and the soluble secretome obtained from mating gametes. PAM is present in vegetative and gametic cell cilia and is released into ectosomes but not into the secretome. In contrast, amidated proGATI is undetectable in vegetative cilia and only appears following gametogenesis. The amidated C-terminal fragment is generated in plus gamete cilia, and released into ectosomes and the secretome during mating; other proGATI products are also variably present in these samples. VLE1 is found in vegetative and plus gamete cilia, but not minus gamete cilia. All ciliary VLE1 is proteolytically processed within the prodomain and amidated. As VLE1 moves to ectosomes and is released into the soluble secretome, it undergoes a change in domain architecture with the catalytic S8 and C-terminal domains dissociating from the amidated N-terminal segment.