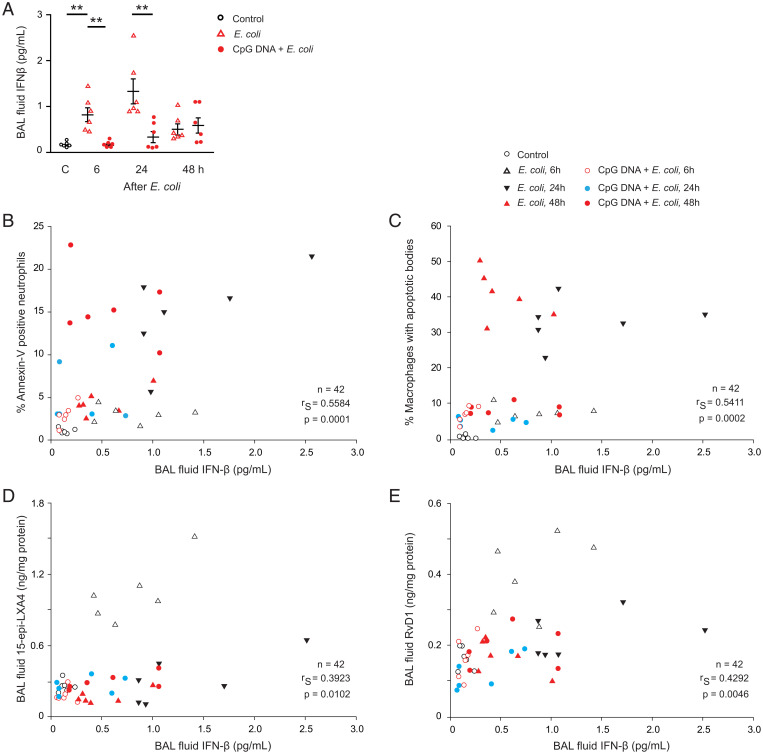
Fig. 4.
Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid levels of IFN-β correlates with neutrophil apoptosis, efferocytosis, and lavage fluid levels of 15-epi-LXA4 and RvD1. Acute lung inflammation was induced in female C57BL/6 mice by intratracheal instillation of 5 × 106 live E. coli with or without simultaneous injection of CpG DNA (1 μg/g b.w., i.p.). Mice were killed at the indicated times and bronchoalveolar lavage was performed. (A) Lavage fluid levels of IFN-β. Results are means ± SEM (n = 6 mice per group). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (Dunn’s multiple contrast hypothesis test). Lavage fluid IFN-β levels positively correlate with the percentage of annexin-V positive neutrophils (gated as Ly6G-positive cells) in lavage fluid (B), the percentage of macrophages containing apoptotic bodies (C), lavage fluid concentrations of 15-epi-LXA4 (D), and RvD1 (E) (Spearman correlation analysis).