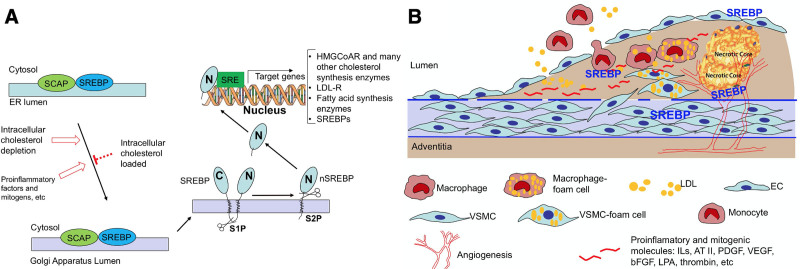
FIGURE 2.
SREBP activation and vasculopathy. SREBP activation in the regulation of cholesterol biosynthesis (A) and its implication in vascular hypercholesterolemia, cell mobilization, and inflammation in the pathogenesis of vasculopathy (B). A, When cells are depleted of lipid/cholesterol or in response to proinflammatory or mitogenic factors, SREBP is escorted by SCAP from the ER to the Golgi apparatus and the SREBP is cleaved by S1P. S1P cleaved SREBP is then further cleaved by S2P to release the active nSREBP from the membrane. The nSREBP enters the nucleus and binds to the SRE of target genes to turn on the expression of the downstream genes including those for cholesterol and fatty acid biosyntheses, LDL-R, and SREBP itself, among others. B, Atherosclerosis or injury-induced neointima formation begins with endothelial cell dysfunction or injury. Mitogenic, chemotactic, and proinflammatory factors from the blood circulation and produced locally by dysfunctional vascular cells and inflammatory cells cause further cell dysfunction such as endothelium layer permeability increase, recruitment of circulating monocytes and lymphocytes to subendothelial space, intimal migration of VSMC from the media, formation of foam cells from macrophages and VSMC, and angiogenesis, culminating in intimal hyperplasia and plaque formation. SREBP plays an important role linking inflammation and cellular cholesterol biosynthesis process in the pathogenesis of vasculopathy. AT II indicates angiotensin II; bFGF; basic fibroblast growth factor; EC, endothelial cell; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; HMG CoAR, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase; ILs, interleukins; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; LDL-R, low-density lipoprotein receptor; LPA, lysophosphatidic acid; nSREBP, N-terminal sterol regulatory element-binding protein; PDGF, platelet-derived growth factor; S1P, site-1 protease; S2P, site-2 protease; SCAP, SREBP cleavage-activating protein; SRE, sterol regulatory element; SREBP, sterol regulatory element-binding protein; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VSMC, vascular smooth muscle cell.