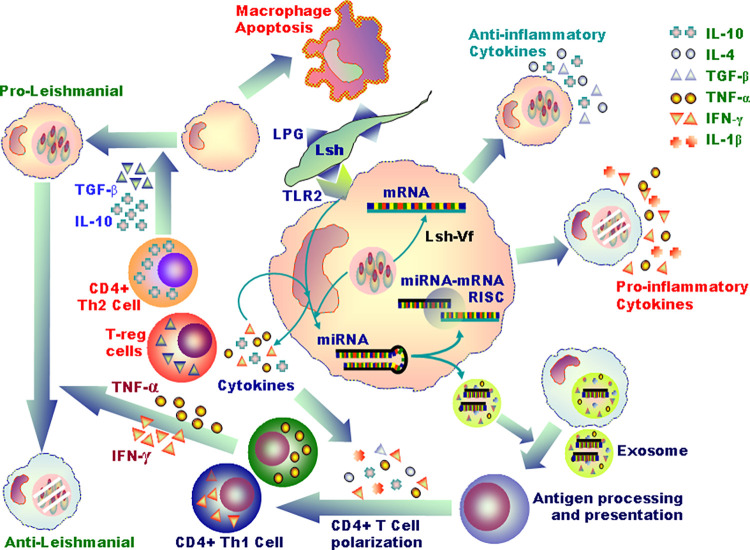
Fig 2. Leishmania-expressed ligands such as LPG interact with corresponding receptors (e.g., TLR2 for LPG) on macrophages and signal altered miRNA expression (at the centre of the figure).
As shown clockwise surrounding the central macrophage, these miRNAs affect macrophage production of proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines, antigen processing and presentation of macrophages, CD4+ T cell polarization into opposing effector subsets, antileishmanial or proleishmanial effects, and macrophage apoptosis or survival. Proleishmanial to antileishmanial functions are induced by the Th1 cell secreted IFN-γ and TNF-α. A balance between these counteractive functions regulated by miRNAs, which can be altered by Leishmania, determines the outcome of the infection. The Leishmania-infected macrophages secrete exosomes filled with different antigens and miRs. The exosomes can be taken up by the neighboring uninfected macrophages, wherein these miRs can execute their functions. The key to the cytokines are shown on the upper right corner of the figure. LPG, lipophosphoglycan; miRNA, microRNA.