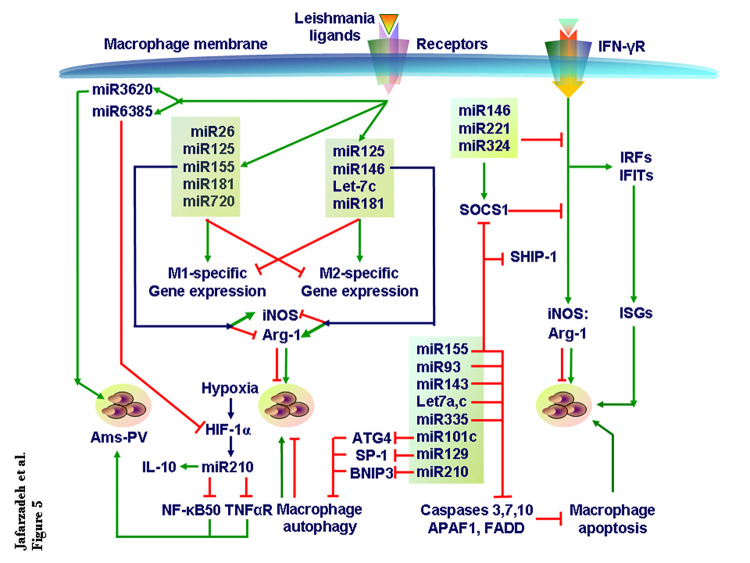
Fig 5. miRNA regulation of Leishmania infection.
TGF-β, and perhaps other cytokines too, regulate miRNA expression in macrophages. As Leishmania infection renders the intracellular environment hypoxic, the HIF-1α induces miR210 to enhance IL-10 production but reduce NF-κB activation and TNF-αR expression to enhance parasite load in the parasitophorous vacuoles in macrophages. Various miRNAs expressed during Leishmania infection modulate cellular processes including cytokine signaling that affects the outcome of Leishmania infection. Similarly, 2 counteractive sets of miRs reciprocally regulate M1 and M2 macrophage subsets differentiation that affects parasite growth. The other miRs regulate macrophage Autophagy and apoptosis and IFN-γR signaling to alter intracellular amastigote numbers. The available literature is too diverse in terms of Leishmania species, macrophage populations, experimental models, and assays to derive a coherent and integrative view of miRs role in Leishmania infection. Therefore, only a fraction of the literature is used to develop the current perspective. HIF-1α, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; miRNA, microRNA.