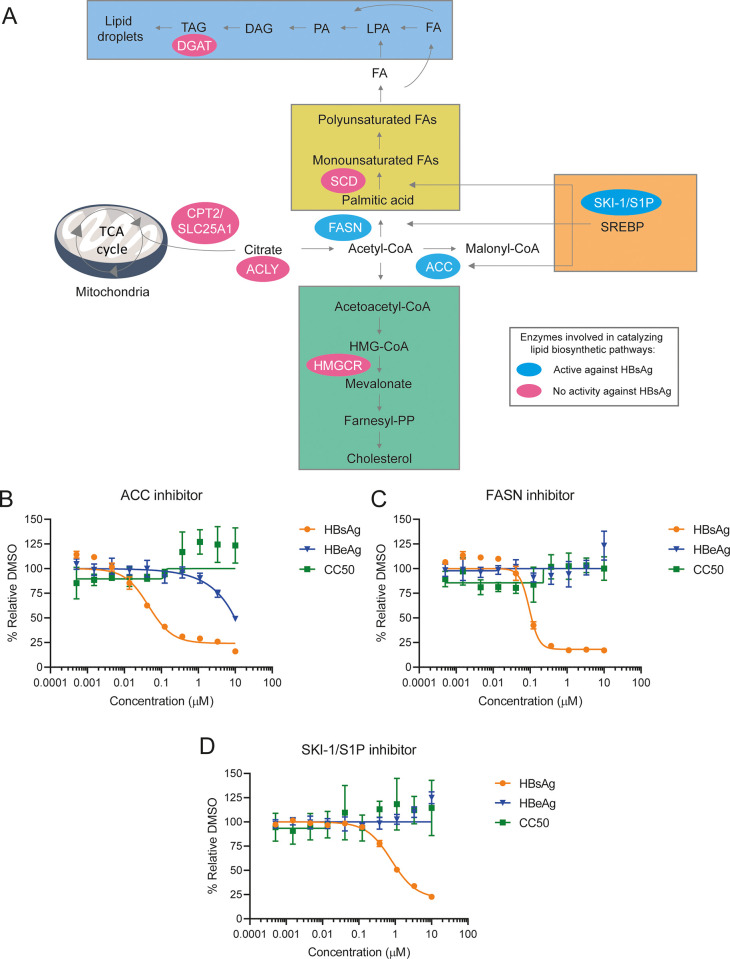
Fig 4. Compounds targeting enzymes within lipid biosynthetic pathways inhibit HBsAg secretion in HepG2-NTCP cells.
(A) Schematic overview of the pathways involved in lipid biosynthesis, such as DNL, TG esterification and cholesterol biosynthesis. The enzymes targeted by compounds that showed anti-HBV activity in HepG2-NTCP cells are indicated with blue ellipse. The enzymes with no activity against HBV in HepG2-NTCP cells are indicated with pink ellipse. (B-D) HepG2-NTCP cells infected with HBV for three days were treated with selected compounds in an eight-point dose response. After three days of treatment, extracellular HBsAg and HBeAg levels as well as cell viability were measured. Effect of ACC (B), FASN(C) and SKI-1/S1P (D) inhibitors on extracellular HBsAg and HBeAg and cell viability in HBV-infected HepG2-NTCP cells. Results are presented as mean and standard deviation (SD).