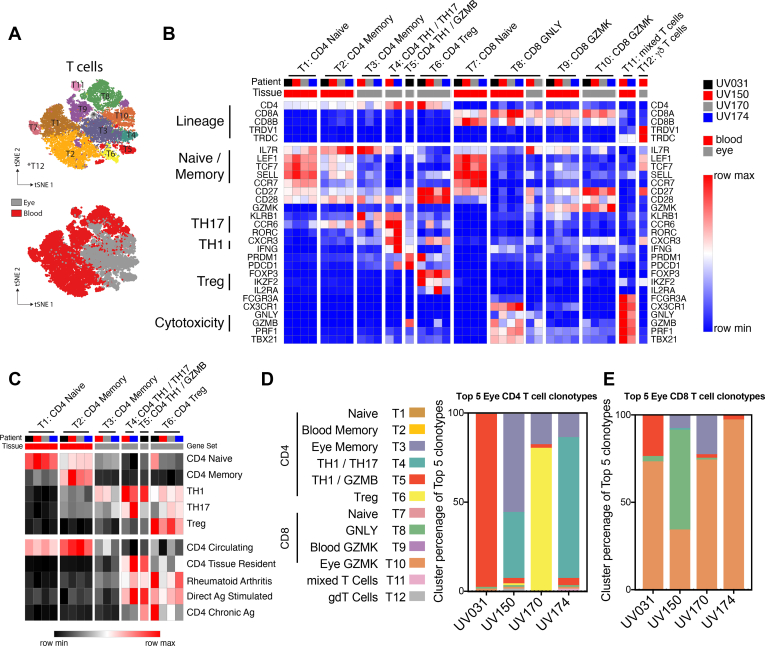
Figure 3.
CD4 T cells show individualized combinations of ocular TH1, TH1/TH17, and regulatory T (Treg) cells, whereas CD8 T cells share a common transcriptional program. Gene expression in effector CD4 T cells reflects both patient-to-patient variation and shared signatures of tissue residency, antigen exposure, and rheumatoid arthritis. In contrast, ocular CD8 T cells across patients share increased expression of intermediate differentiation markers and reduced expression of classic cytotoxic molecules. A, Diagram showing t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding subanalysis of blood and ocular T cells colored by cluster (top panel) or tissue source (bottom panel). B, Heatmap representation of relative gene expression of cluster-defining genes (rows) for each patient (columns black, red, grey, blue) and tissue (blood, red; eye, grey). Clusters are annotated with cell lineages defined above. Samples with less than 5% contribution to each cluster were excluded. Clusters are annotated with lineage and functional subset. Genes defining specific T-cell states or functions are indicated. C, Heatmap representation of relative expression of cell lineage or state-defining gene set expression between T-cell clusters. D, E, Bar graphs showing percent of T-cell cluster occupancy for the top 5 ocular (D) CD4 and (E) CD8 T-cell clonotypes.