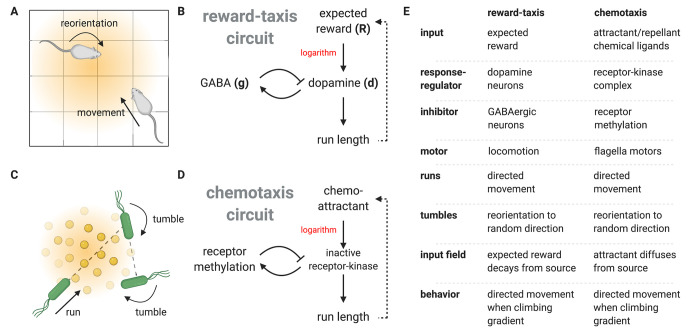
Fig 4. Dopamine regulation of behavior in the model is analogous to bacterial chemotaxis.
(A) The behavior of an animal in an open field is modelled as a series of directed movements (runs). The direction of each run is chosen at random (or, more generally, stops between runs decorrelate motion direction), and the duration of each run increases with dopamine level. (B) Dopamine is controlled by an FCD circuit activated by expected reward. (CD) The reward-dopamine-behavior circuit is analogous to the chemotaxis circuit that underlies bacterial navigation towards chemo-attractants. Bacterial motion is composed of a series of runs. The direction of each run is randomized by tumbling events, and run duration increases with the inactivation of a receptor-kinase complex, which is controlled by an FCD circuit activated by chemoattractant concentration. (E) Table detailing the mapping between the dopamine system and the chemotaxis system. Figures were created with BioRender.com.