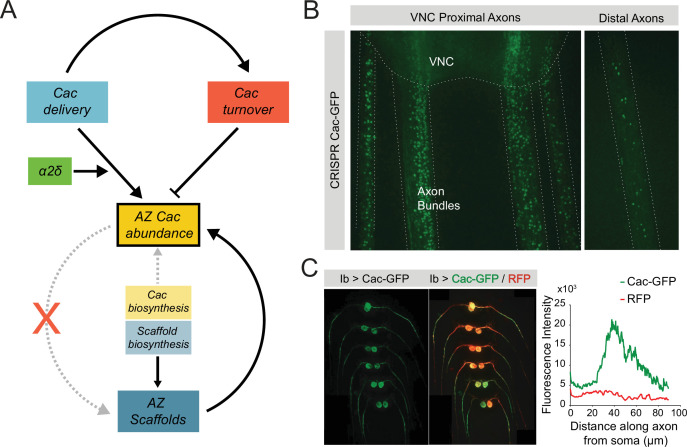
Figure 8. Model of Cac and active zone (AZ) scaffold regulation at the Drosophila neuromuscular junction (NMJ).
(A) AZ Cac abundance (yellow box) is regulated by both new Cac delivery (blue box) and Cac turnover from AZs (red box). Cac delivery is positively regulated by α2δ, and new delivery promotes turnover of existing channels. Cac biosynthesis (light yellow box) weakly regulates AZ Cac abundance, as AZ abundance is buffered against moderate changes in biosynthesis. In contrast, scaffold biosynthesis is a strong regulator of AZ scaffold abundance. The dependence relationship between AZ Cac abundance and AZ scaffold abundance is unidirectional: AZ scaffolds regulate Cac accumulation, but Cac is dispensable for AZ scaffold formation. (B) Left – representative image of endogenously tagged Cac-GFP puncta in axon bundles proximal to the ventral nerve cord (VNC). Right – representative image of Cac-GFP in distal axons. These axon puncta are immobile over a period of 30 min. (C) Left – representative image of a VNC with Cac-GFP (green) and RFP (red) expressed exclusively in MN1-Ib neurons. Right – quantification of Cac-GFP and RFP signal intensity as a function of distance along the axon from the soma. Plotted signal intensity was averaged across eight axons. RFP intensity is constant throughout the first 100 µm, while Cac-GFP intensity is elevated in the 30–60 µm range.