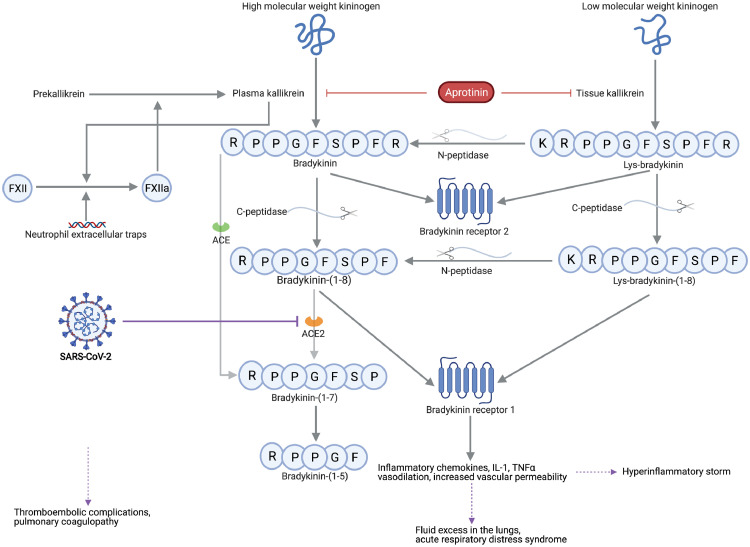
Figure 1.
The kallikrein-kinin system links coagulation and inflammation in COVID-19.
The metabolic pathway of bradykinin, Lys-bradykinin and their metabolites. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) causes downregulation and functional deficiency of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), which could impair the degradation of kinin peptides that act on bradykinin receptor 1. Excessive activation of bradykinin receptor 1 results in both hyperinflammatory responses and pulmonary edema, whereas factor XII (FXII) activation leads to coagulation activation and provides a feedback loop with activation of the kallikrein-kinin pathway. Aprotinin inhibits plasma and tissue kallikrein, in addition to its in vitro observed antiviral actions. ACE indicates angiotensin-converting enzyme; C-peptidase, carboxypeptidase; IL-1, interleukin-1; N-peptidase, aminopeptidase; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor alpha. This figure was created with BioRender.