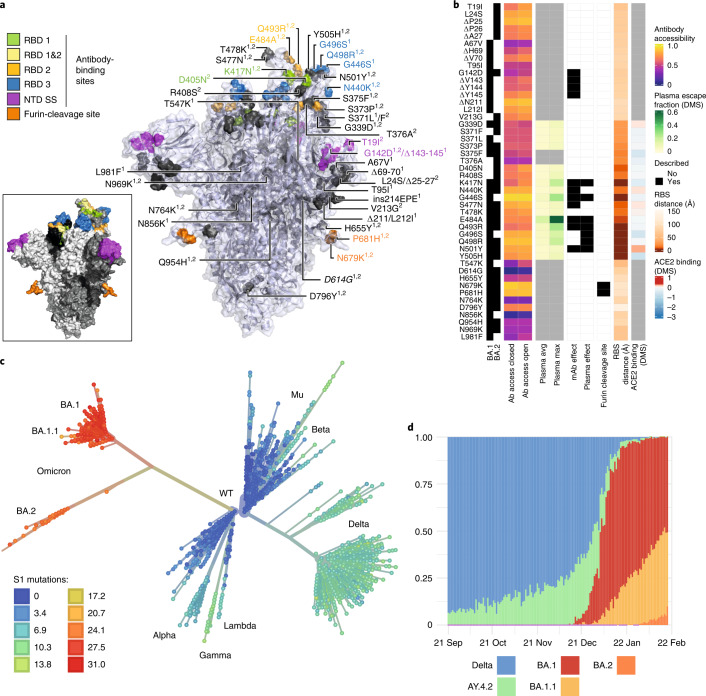
Fig. 1. Spike amino acid changes, phylogeny and emergence of the Omicron variant.
a, Spike homotrimer in open conformation with locations of Omicron substitutions, deletions (Δ) or insertions (ins) present in the lineages BA.1 and BA.2 (superscripts 1,2). Mutated residues highlighted as spheres with opaque surface representation. Residues impacting RBD-specific antibodies of classes 1, 2 or 391; belonging to the NTD antibody supersite (NTD SS)26; or comprising the furin-cleavage site, are coloured, the remainder in grey. Inset shows the wider extent of these sites, with remaining areas of the protein shaded to show the three monomers. Mutations are annotated on the monomer with an ‘up’ receptor-binding domain with D614G (italicized), which is shared by common descent by all lineage B.1 descendants. Visualization uses a complete spike model84 based on a partial cryo-EM structure (RCSB Protein Data Bank (PDB) ID: 6VSB92). b, Heat maps showing properties of amino acid residues in the Omicron variants BA.1 and BA.2. Structure-based epitope scores87 for residues in the spike structure in closed and open conformations are shown. For RBD residues, DMS studies show the escape fraction (quantitative measure of the extent to which a mutation reduced polyclonal antibody binding) for each mutant-averaged (‘plasma average’) and most sensitive plasma (‘plasma max’)20. Each mutation is classified as having mutations affecting neutralization by either monoclonal antibodies (mAbs)27,85,93,94,95 or antibodies in convalescent plasma (infected or vaccinated20,85,95,96). Membership of the furin cleavage site is shown. Distance to ACE2-contacting residues forming the receptor-binding site (RBS) is shown (‘RBS’ is residues with an atom <4 Å of an ACE2 atom in the structure of RBD bound to ACE2) (RCSB PDB ID: 6M0J86). ACE2 binding scores represent the binding constant (Δlog10 KD) relative to the wild-type reference amino acid from DMS experiments97. c, Inferred evolutionary relationships of SARS-CoV-2 from NextStrain (https://nextstrain.org/ncov/gisaid/global), with the VOCs labelled. Tree tip colours correspond to the number of mutations causing spike amino acid substitutions relative to the Wuhan-Hu-1 (lineage B) sequence. d, The proportion of genome sequences from Scotland sampled between 1 September 2021 and 29 January 2022 is shown: ‘Delta’ includes all B.1.617.2 and AY assigned sequences that are not in the Delta sub-lineage AY.4.2 (defined by spike mutations Y145H and A222V), and BA.1, BA.1.1 and BA.2 are Omicron sub-lineages.