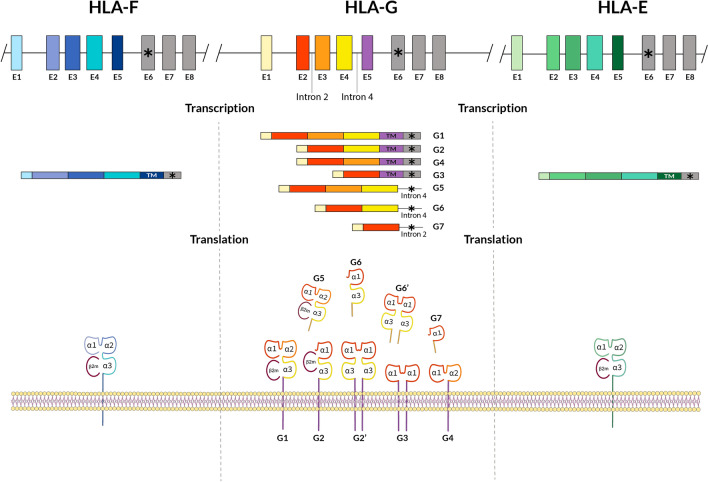
Fig. 1.
HLA gene complex is located in the short arm of human chromosome 6 (6p21.3). HLA-G, -E and -F mRNA transcription and translation scheme and HLA-G membrane and soluble isoforms are shown (see text). Exons (E) of each gene are shown in upper panels of the figure. A (*) symbol indicates a stop codon: it may be localized in E6 in HLA-E, -F and -G genes. HLA-G also presents stop codons in intron 2 or intron 4 depending on alternative splicing process which gives rise to different isoforms. Stop codon may be maintained in mature mRNA due to a reading-through mechanism in humans and primates which is described also in other HLA genes (i.e., HLA-DRB6). The presence of a selenocysteine insertion sequence (SECIS) at the 3 untranslated region leads to a selenocysteine incorporation at UGA (stop) codons [15–18]; this may be the cause for stop codon maintenance in HLA-G, -E and -F translation. Beta-2 microglobulin (β2m) is represented bound to protein molecules in purple color. See also references [19, 20]