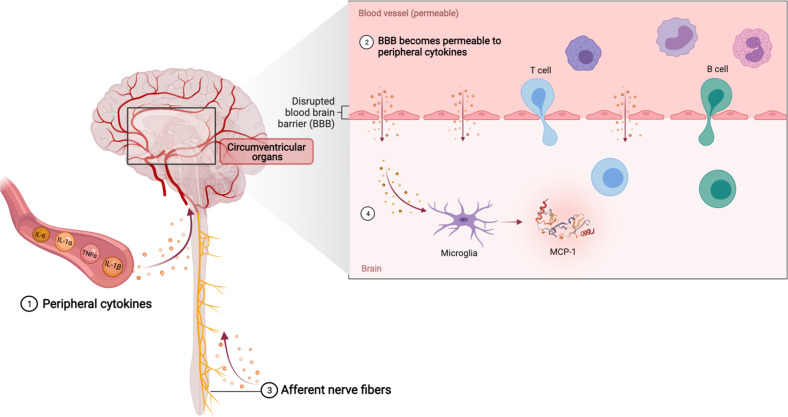
Fig. 3. Trafficking of peripheral inflammatory signals to brain.
(1) Active transport of peripheral cytokines. (2) Passage of peripheral cytokines through leaky regions of blood–brain barrier (BBB). (3) Transmission of peripheral cytokine signals to the brain by activated cytokine receptors on afferent nerve fibers. (4) Trafficking of peripheral cell types (e.g., monocytes, macrophages, and T cells) in response to monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP-1) release by activated microglia.