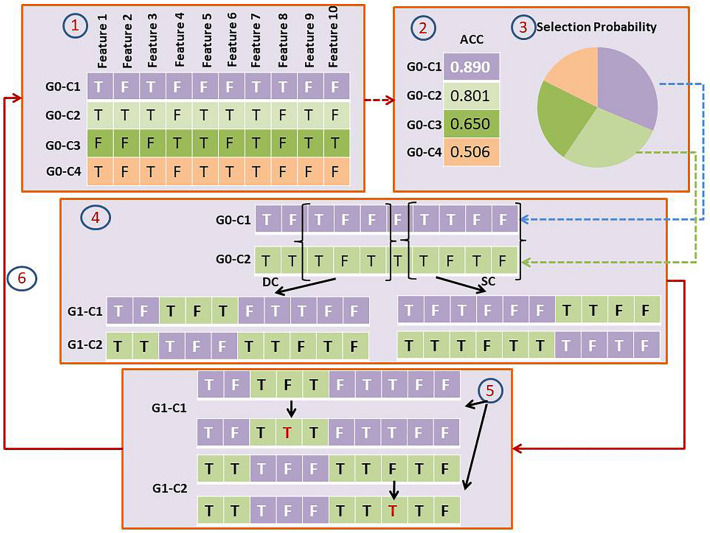
Figure 2.
The Genetic Algorithm workflow. The steps are: (1) Generation of the initial population of solutions; (2) Evaluation of fitness values of each solution within the population; (3) The “mating” process of the solution, in which the probability of a solution to be selected is proportional to the estimated fitness value; (4) The random designation of crossover points on each vector of solution during the “mating” process. SC and DC stand for Single- and Double-Crossover, respectively; (5) The introduction of random mutations on the crossover-ed solution vectors; (6) The replacement of the entire population by daughter solutions.