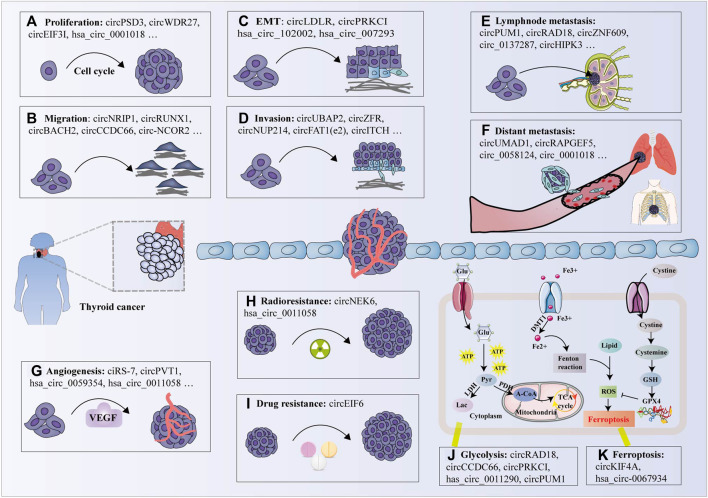
FIGURE 3.
Biological functions of circRNAs in thyroid cancer. (A) circRNAs promote cell proliferation by promoting (e.g., circPSD3) or inhibiting (e.g., circITCH); (B) circRNAs promote cell migration by facilitating (e.g., circNRIP1) or inhibiting (e.g., hsa_circ_0007694); (C) circRNAs modulate the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process by promoting (e.g., circLDLR); (D) Some circRNAs promote cell invasion (e.g., circZFR), while other circRNAs inhibit cell invasion (e.g., circNEURL4); (E) Several circRNAs are correlated with lymphnode metastasis (e.g., circPUM1); (F) A few circRNAs are associated with distant metastasis (e.g., circUMAD1); (G) Some circRNAs have been shown to promote tumor angiogenesis (e.g., ciRS-7) by modulating vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) expression; (H) Several circRNAs facilitate radioresistance in TC cells (e.g., circNEK6); (I) Individual circRNA promotes the drug-resistance of TC cells (e.g., circEIF6); (J) Certain circRNAs modulate glycolysis (e.g., circRAD18); and (K) ferroptosis (e.g., circKIF4A) in thyroid cancer cells. Glu: glucose, ATP: adenosine triphosphate, Pyr: pyruvate, Lac: lactate, LDH: lactate dehydrogenase, PDH: pyruvate dehydrogenase, A-CoA: acetyl-CoA, TCA cycle: tricarboxylic acid cycle, GSH: glutathione, ROS: reactive oxygen species, GPX4: glutathione peroxidase 4.