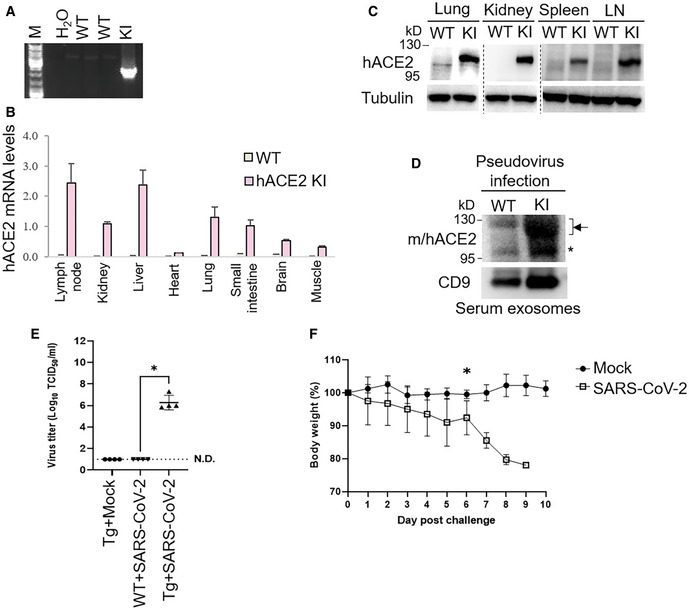
Figure EV4. Infection of hACE2 knockin mice and EF1α‐hACE2 transgenic mice with SARS‐CoV‐2 pseudovirus or live SARS‐CoV‐2.
-
APCR analyses of hACE2 knockin allele in the genomic DNA from mouse tails. The PCR product of the 2,379‐bp band indicates the hACE2 knockin allele.
-
BReal‐time PCR analyses of knockin human ACE2 (hACE2) mRNA levels in the lymph nodes, kidneys, liver, heart, lungs, small intestine, brain, and muscle from wild‐type or hACE2 KI mice. The human ACE2 mRNA levels were normalized to mouse GAPDH mRNA levels. n = 2 (technical replicates) per group.
-
CImmunoblotting analyses of GLK, tubulin, and human ACE2 proteins in the lungs, kidneys, spleen, and lymph nodes of wild‐type and hACE2 KI mice.
-
DImmunoblotting of ACE2, GLK, and CD9 proteins in the exosomes isolated from the sera of the SARS‐CoV‐2 pseudovirus‐infected mice. Exosomes were isolated sequentially using ExoQuick kits and then ExoQuick ULTRA columns. Arrowheads denote glycosylated ACE2 proteins; asterisk denotes unglycosylated ACE2 proteins.
-
E, FEF1α‐hACE2 Tg and wild‐type mice were infected intranasally with 2 × 105 pfu of live SARS‐CoV‐2. n = 4 (biological replicates) per group. EF1α‐hACE Tg mice were treated intranasally with PBS (Mock) as controls. On day 3 postinfection, the mice were sacrificed, and the lung tissues were homogenized for the TCID50 assay (E). The survival rate of EF1α‐hACE2 Tg mice challenged with live SARS‐CoV2 was monitored (F). WT, wild‐type mice; KI, hACE2 knockin mice; Tg, EF1α‐hACE2 transgenic mice. The number of infected mice was less than 3 from day 7 due to deaths; thus, the statistical analysis of panel F was only performed on data up to day 6 postinfection.
Data information: In (B), data are presented as means ± SD. In (E), data are presented as means ± SEM. *P‐value < 0.05 (Kruskal–Wallis test). In (F), data are presented as means ± SEM. *P‐value < 0.05 (Mann–Whitney test).
