Figure 5.
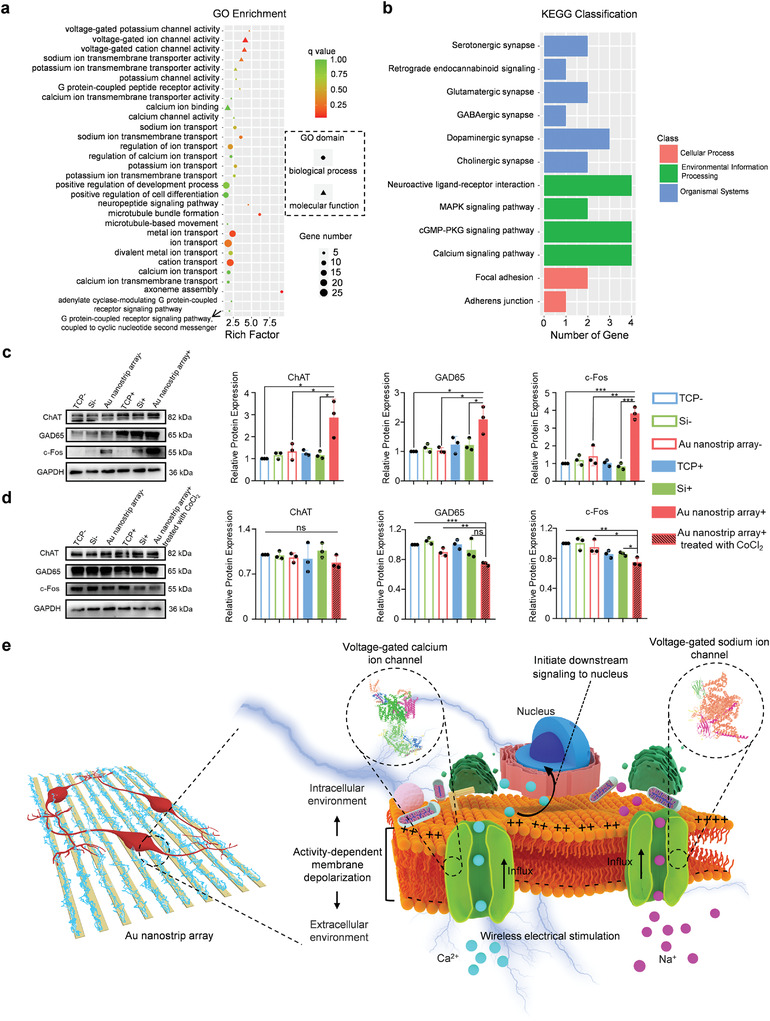
Mechanism underlying NSC differentiation promoted by the Au nanostrip‐based wireless device. a) GO functional enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes between the Au nanostrip array+ and TCP‐ groups. b) KEGG pathway classification of differentially expressed genes between the Au nanostrip array+ and TCP‐ groups. c) Western blot analysis of the ChAT, GAD65, and c‐Fos protein expression of NSCs seeded on TCP, Si, or Au nanostrip array and cultured without or with rotating magnetic field (300 rpm) on day 5. Glyceraldehyde 3‐phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was used as the housekeeping gene. Quantitative analysis data obtained using Image J software are presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 4); ns p > 0.05, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. d) Western blot analysis of ChAT, GAD65, and c‐Fos protein expressions by NSCs seeded on TCP, Si, or Au nanostrip array and cultured without or with rotating magnetic field (300 rpm) on day 5. The NSCs in the Au nanostrip array+ group were treated with 3 × 10−3 m CoCl2 before the rotating magnetic field was applied. GAPDH was used as the housekeeping gene. Quantitative analysis data acquired by Image J software are presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 4); ns p > 0.05, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. e) Diagram of the mechanism of NSCs differentiation promoted by the Au nanostrip‐based wireless device.
