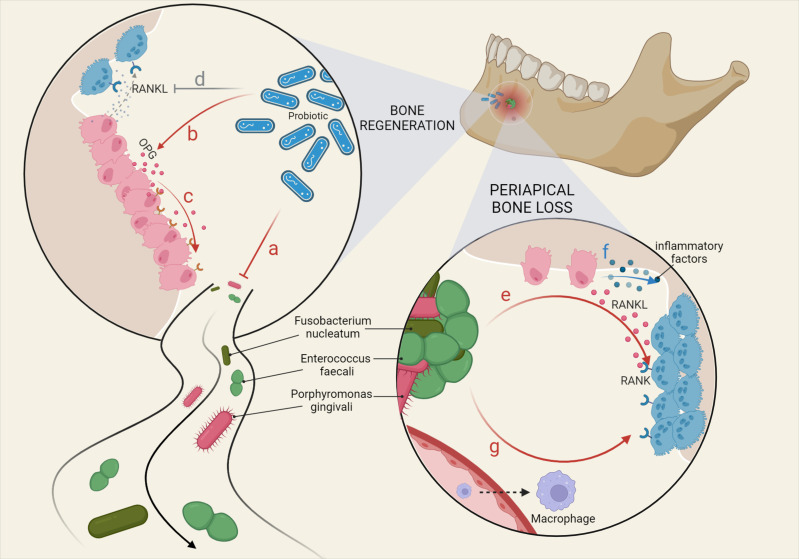
Figure 1.
Main microbial factors affecting bone remodeling in CAP. Various oral microorganisms ultimately affect the inflammatory response and bone damage in the periapical region by influencing the physiological functions of macrophage differentiation and osteoblast and osteoclast metabolism. Bone regeneration: (A) Probiotics inhibit pathogenic bacteria. (B) Probiotics promote OPG expression by OBs. (C) OPG competitively inhibits the binding of RANK to RANKL. (D) Probiotics downregulate RANKL produced by OBs. Periapical bone loss: (E) Fusobacterium nucleatum and Enterococcus faecali stimulate OBs to produce RANKL, binding to RANK on OCs. (F) OBs are stimulated to secrete a variety of inflammatory factors, triggering greater bone loss. (G) LPS recruits macrophages from the blood and LTA promotes the differentiation of macrophages towards OCs.