Fig. 1.
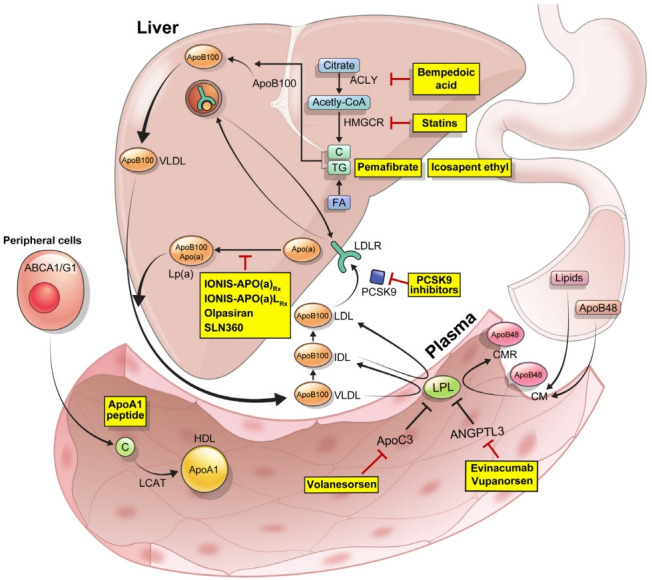
Sites and targets of new lipid-lowering agents. In the small intestine, lipids and apolipoprotein B48 (ApoB48) are packaged into chylomicron (CM) particles. In the liver, bempedoic acid inhibits an enzyme ATP citrate lyase (ACLY), which is responsible for the conversion of citrate and coenzyme A (CoA) to oxaloacetate and acetyl-CoA. Pemafibrates are selective peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα) modulators, which initiate β-oxidation, reduce triglyceride (TG) content, and enhance lipoprotein lipase (LPL) activity. Omega-3 fatty acids also exhibit their effects through the PPAR-mediated pathway. Recycling of low-density lipoprotein receptors (LDLRs) is increased by the inhibition of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9). In the plasma, TGs within the CM and very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) are hydrolyzed by LPL, inhibitors of which include apolipoprotein C3 (ApoC3) and angiopoietin-like 3 (ANGPTL3). Volanesorsen is an antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) targeting the ApoC3. Evinacumab is a monoclonal antibody which targets ANGPTL3. Vupanorsen is a triantennary N-acetylgalactosamine carbohydrates (GalNAc)-conjugated ASO which targets ANGPTL3 mRNA. Binding of apolipoprotein (a) (Apo(a)) to apolipoprotein B100 (ApoB100) an LDL-like moiety forms lipoprotein(a) (Lp(a)). IONIS-APO(a)Rx and IONIS-APO(a)LRx are ASOs targeting the Apo(a). Olpasiran and SLN360 are small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) targeting the Apo(a). In the peripheral cells, apolipoprotein A1 (ApoA1) present in small high-density lipoprotein (HDL) mobilizes intracellular cholesterol (C) and is assisted by ATP-binding cassette protein A1 (ABCA1) and ATP-binding cassette protein G1 (ABCG1), after esterification by lecithin cholesterol acyl transferase (LCAT). ApoA1 peptide induces C efflux. CMR, chylomicron remnant; FA, fatty acid; HMGCR, 3-hydroxy3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase; IDL, intermediate-density lipoprotein.
