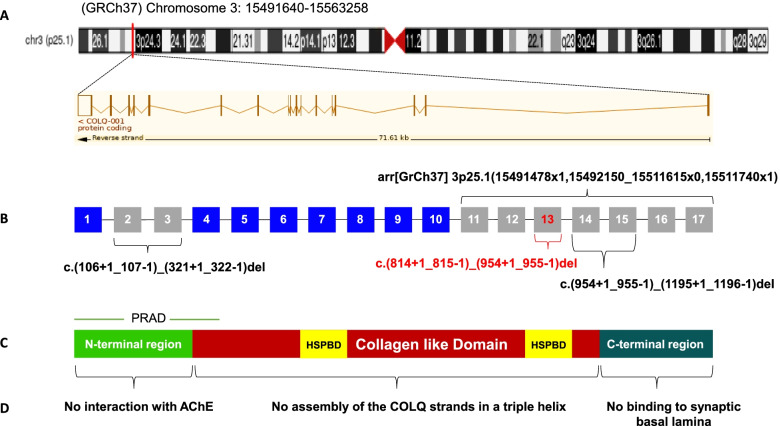
Fig. 5.
Schematic representation of COLQ domains and the CNV mutations reported in this gene. A Genomic location of COLQ gene (from UCSC browser GRCh37/hg19: http://genome.ucsc.edu) with the full transcript contains 17 coding exons (from the Ensembl database GRCh37 release 107 - Jul 2022). B COLQ exons with the three published pathogenic CNVs in the literature and the deletion described in this study (showed in red color). C Primary structure of COLQ with its three protein domains. D Consequences of mutations in human COLQ protein [11, 32]. Mutations in the N-terminal proline-rich attachment domain (PRAD) prohibit the association of each COLQ strand with an acetylcholinesterase tetramer. Mutations in the central collagen domain containing two heparan sulfate proteoglycan binding (HSPBP) domains cause loss of assembly of the COLQ strands in a triple helix, and mutations in the C-terminal region lead to the synthesis of single- or triple-strands of COLQ-AChE, which are unable to bind to the basal lamina [3, 9, 12, 33].