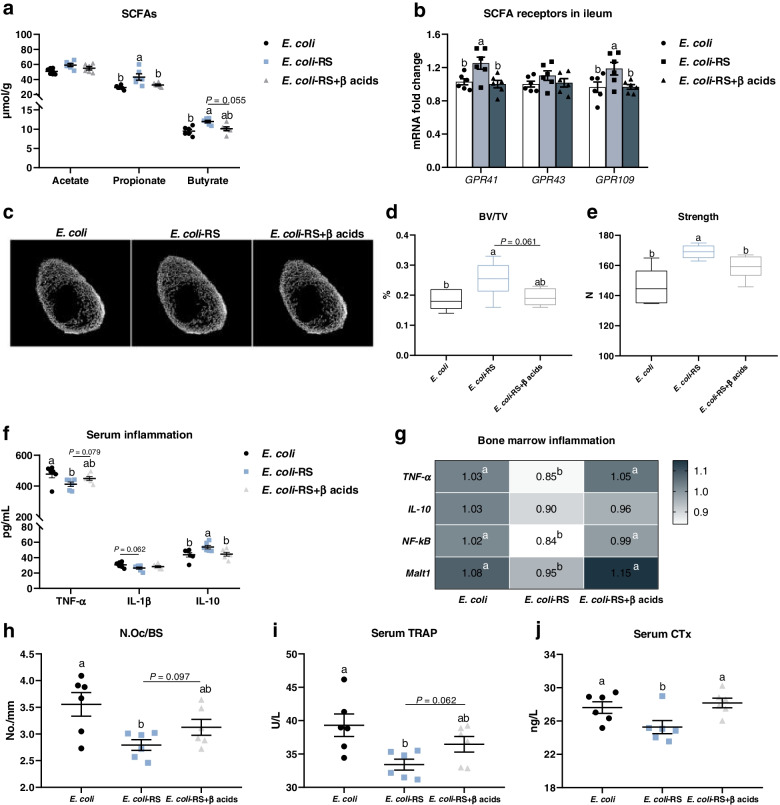
Fig. 5.
β acid eliminates the improved roles of RS on E. coli-induced bone loss via increasing bone resorption. a The changes in the levels of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) in cecal content and (b) in the SCFA receptor gene expression including G protein-coupled receptors 41 (GPR41) and GPR43 in ileum. c Representative micro-CT images and the quantification of (d) bone volume/total volume (BV/TV) of proximal tibia and (e) strength. f Serum tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-10 were detected by ELISA. g The inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-10, nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation protein 1 (Malt1) mRNA expression in bone marrow from different groups. h The number of osteoclast (N.Oc/BS) in proximal tibias and circulating bone resorption markers, including (i) tartrate resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) and (j) C-terminal cross-linked telopeptide of type I collagen (CTx), were also determined. Data are expressed as mean and standard deviation.a,bMean values with different letters are significantly different by one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s post hoc test (P < 0.05)