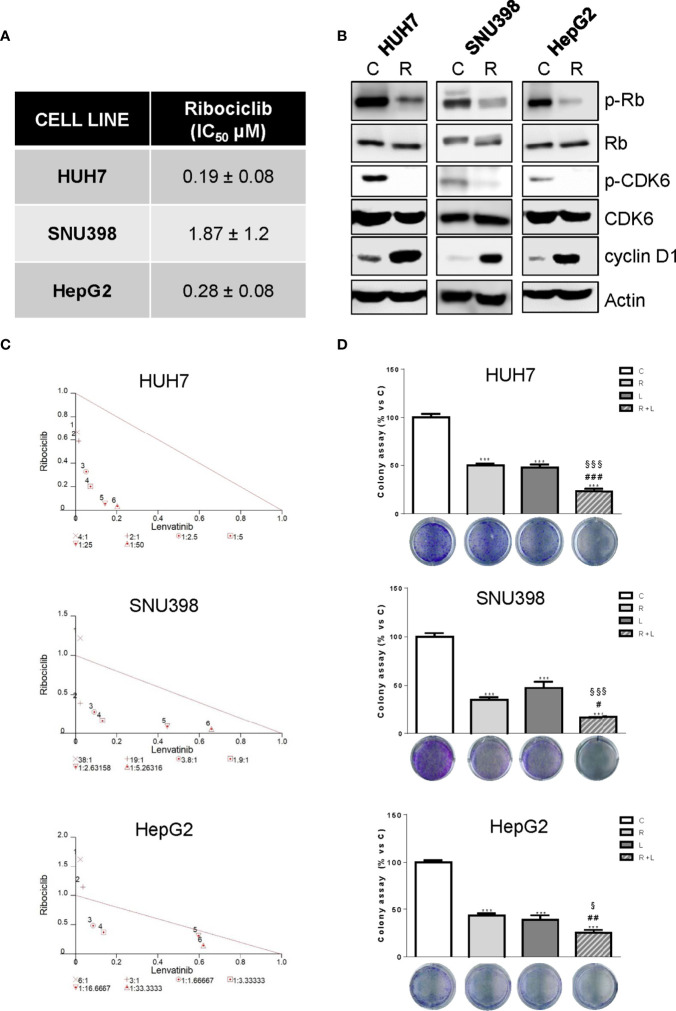
Figure 3.
Ribociclib and lenvatinib combination exerts additive anti-proliferative effects in HCC cells and inhibits colony formation more strongly than single agents. (A) After 24h from seeding, HUH7, SNU398, and HepG2 cells were treated with increasing concentrations of ribociclib (R) for 6 days. Cells proliferation was evaluated by CV assay and the IC50 values were calculated using GraphPad Prism 6.00 software. (B) HCC cells were untreated (C) or treated with 1 μM R for 24h. The cells were lysed and the expression of the indicated proteins was evaluated by Western blot analysis. (C) Cells were treated with R, L or the combination. The growth medium with drugs was refreshed every 3 days. After 6 days, cell proliferation was assessed by CV assay. Combination indexes were calculated with Calcusyn software. (D) HUH7, SNU398, and HepG2 cells were treated with R or L at their corresponding IC50 values alone or in combination. After 6 days, colony formation was assessed by CV assay. Representative images of crystal violet staining of colonies are shown. ***p<0.001 vs C; #p<0.05, ##p<0.01 ###p<0.001 vs R; §p< 0.05, §§§p<0.001 vs L. Data in A are mean values ± SD of three independent experiments. Data in B-C are representative of two independent experiments. Data in D are mean values ± SD of two independent experiments.