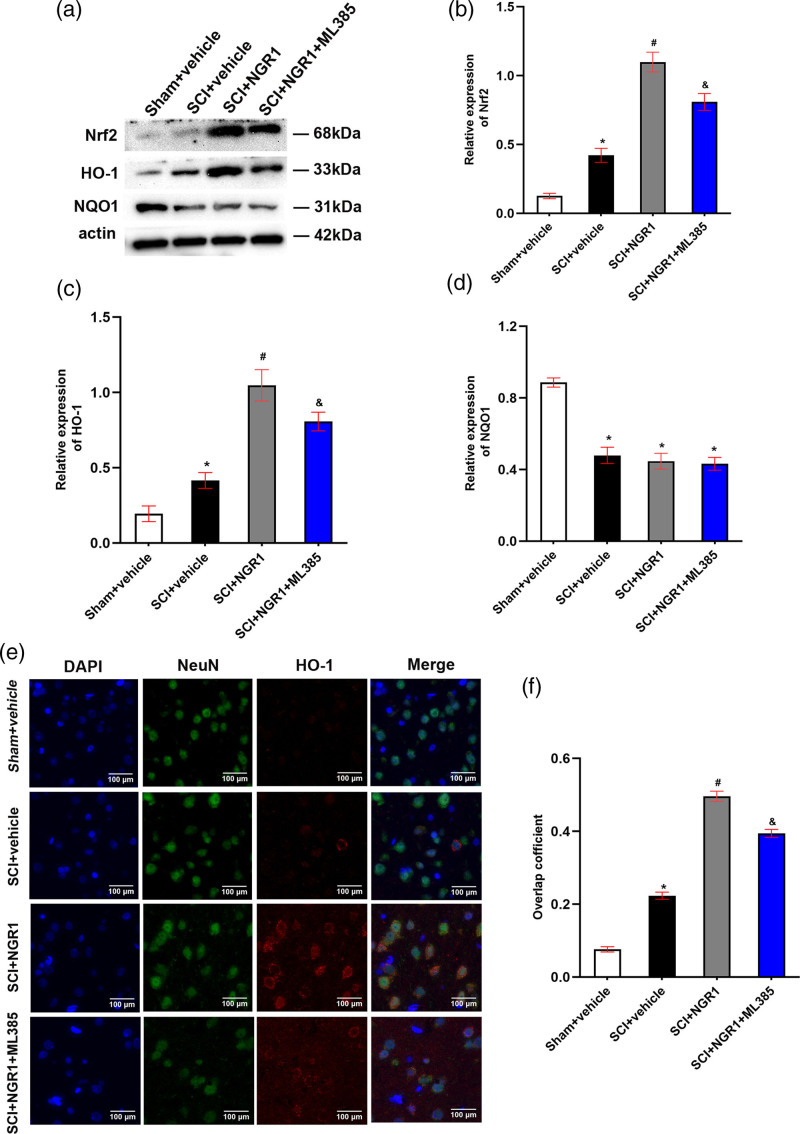
Fig. 3.
NGR1 administration activates Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway after SCI. (a) The representative image of Western Blot analysis for Nrf2, HO-1, and NQO1 in the Sham + vehicle, SCI + vehicle, SCI + NGR1, and SCI+NGR1+ML385 groups at 21 days after SCI. (b–d) Quantitative analysis of Nrf2/actin, HO-1/actin, and NQO1/actin in each group. N = 3. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. One-way analysis of ANOVA with Turkey’s post hoc tests was used. *P < 0.05 vs. the Sham + vehicle group; #P < 0.05 vs. the SCI + vehicle group; &P < 0.05 vs. the SCI + NGR1 group. (e) The representative image of immunofluorescence analysis for HO-1 in the Sham + vehicle, SCI + vehicle, SCI + NGR1, and SCI + NGR1 + ML385 groups at 3 days after SCI. Bars = 100 μm (400×). (f) Quantitative analysis of the overlap coefficient in each group. N = 3. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 vs. the Sham + vehicle group; #P < 0.05 vs. the SCI + NGR1 group. ANOVA, analysis of variance; HO-1, heme oxygenase-1; NGR1, notoginsenoside R1; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2 related factor 2; NQO1, anti-NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase 1; SCI, spinal cord injury.