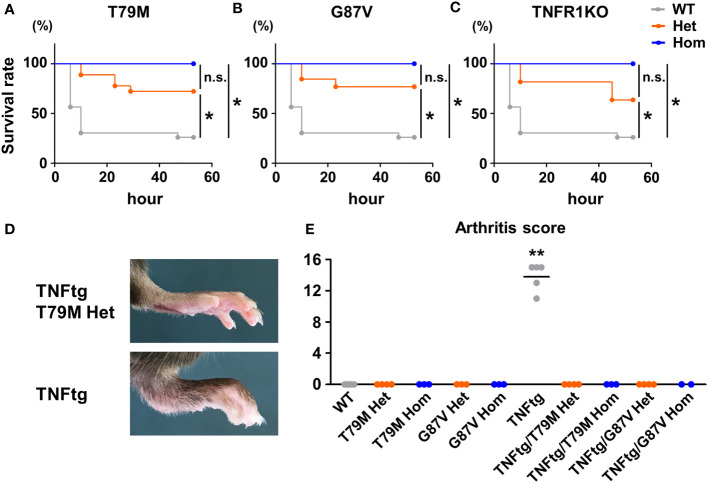
Figure 2.
TRAPS mutations strongly suppressed lethal response by LPS and D-galactosamine and diminished TNFα-mediated arthritis. (A-C) T79M and G87V TRAPS mutant mice and TNFR1 KO mice were intraperitoneally administrated with LPS (100 μg/kg body weight) and D-galactosamine (400 mg/kg body weight). Survival rates of the mice after the administration of LPS and D-galactosamine. Survival rates of WT (n = 23), T79M strain (A); Het (n =18), Hom (n = 9), G87V strain (B); Het (n =13), Hom (n = 13), and TNFR1 KO strain (C); Het (n =11), Hom (n = 9). Gray, orange, and blue lines indicate WT, heterozygotes, and homozygotes, respectively. p-values for the differences between subgroups of mice were calculated by log-rank test using stratified analysis. (D, E) T79M or G87V mutant mice were crossed with TNFtg mice, and the severity of arthritis was evaluated. WT (n = 5), T79M Het (n = 4), T79M Hom (n = 3), G87V Het (n = 3), G87V Hom (n = 3), TNFtg (n = 5), TNFtg/T79M Het (n = 4), TNFtg/T79M Hom (n = 3), TNFtg/G87V Het (n = 4), TNFtg/G87V Hom (n = 2). (D) Representative images of the hind paw of TNFtg T79M heterozygous mouse and TNFtg mouse. (E) Arthritis scores of the mice at the age of 17 weeks. **p<0.01 vs. any other groups. WT, wild-type; TNFtg, TNFα transgenic; TNFα, Tumor necrosis factor α; TRAPS, TNF receptor-associated periodic syndrome; IL, interleukin; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; TNFR1, TNF receptor type I; TNFtg, Human TNFα-transgenic mice; Het, heterozygote; Hom, homozygote. *p<0.01; n.s., not significant.