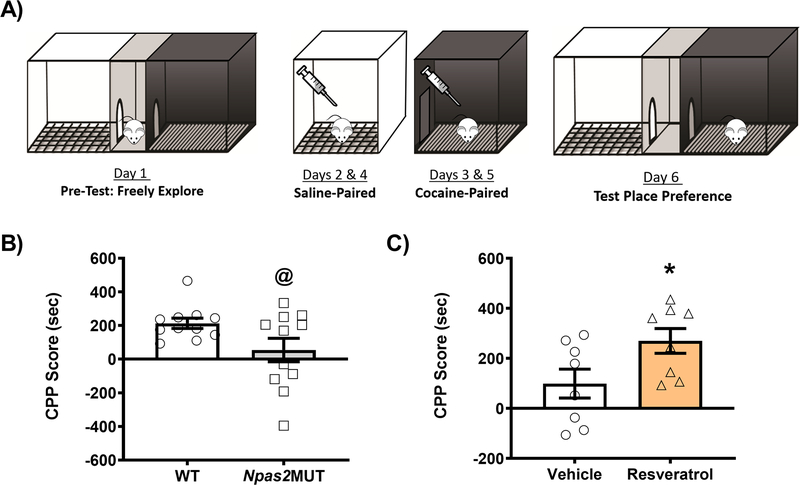
Figure 3. NPAS2 and SIRT1 are important for cocaine preference.
(A) Schematic showing the cocaine conditioned place preference (CPP) paradigm. Mice were conditioned to saline (10 ml/kg, i.p.) or cocaine (5 mg/kg, i.p.) on conditioning days. (B) Npas2 mutant mice show decreased cocaine preference relative to wild-type (WT) littermates. (C) C57BL/6J mice were administered vehicle or resveratrol (20 mg/kg; i.p.) 30 minutes before conditioning. Mice administered resveratrol showed a significant increase in cocaine preference relative to vehicle controls. Data represented as Mean ± SEM (n= 8–11). CPP score is calculated by subtracting the initial pre-test time in the cocaine paired chamber from the same chamber’s test-day time (i.e., Test cocaine-paired time minus Pre-Test cocaine-paired time). Asterisk indicates significance relative to controls (* p<0.05). At-sign indicates a trend towards significance (@, p=0.0504).