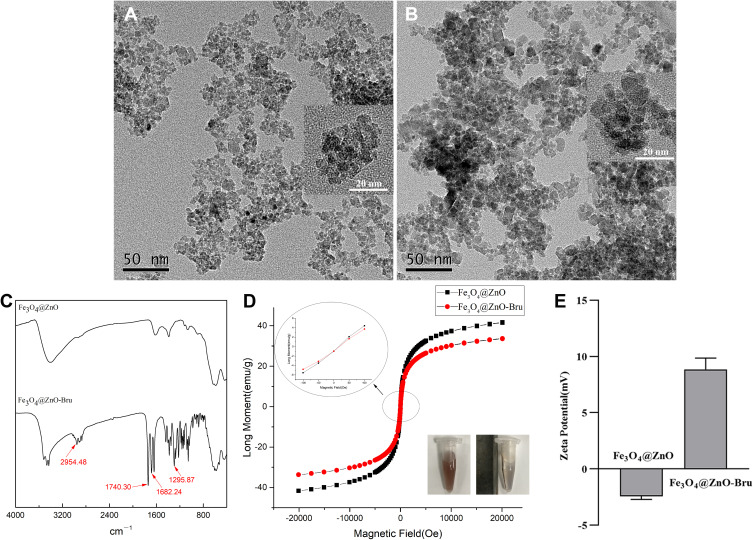
Figure 2.
Characterization of Fe3O4@ZnO NCs and Fe3O4@ZnO-Bru NCs. (A and B) TEM images of Fe3O4@ZnO NCs (A) and Fe3O4@ZnO-Bru NCs (B). Scale bar: 50 nm. Insert: TEM image with a larger magnification, scale bar: 20 nm; (C) FTIR of Fe3O4@ZnO NCs and Fe3O4@ZnO-Bru NCs; (D) Magnetic hysteresis loops of Fe3O4@ZnO NCs and Fe3O4@ZnO-Bru NCs. The saturation of Fe3O4@ZnO-Bru slightly decrease compared with Fe3O4@ZnO but is still superparamagnetic, indicating that our drug delivery systems have the potential to be directed to a certain area by externally applied magnetism. Insert: The NCs solution was changed from stable to aggregated state under the magnetic field; (E) Zeta potential.