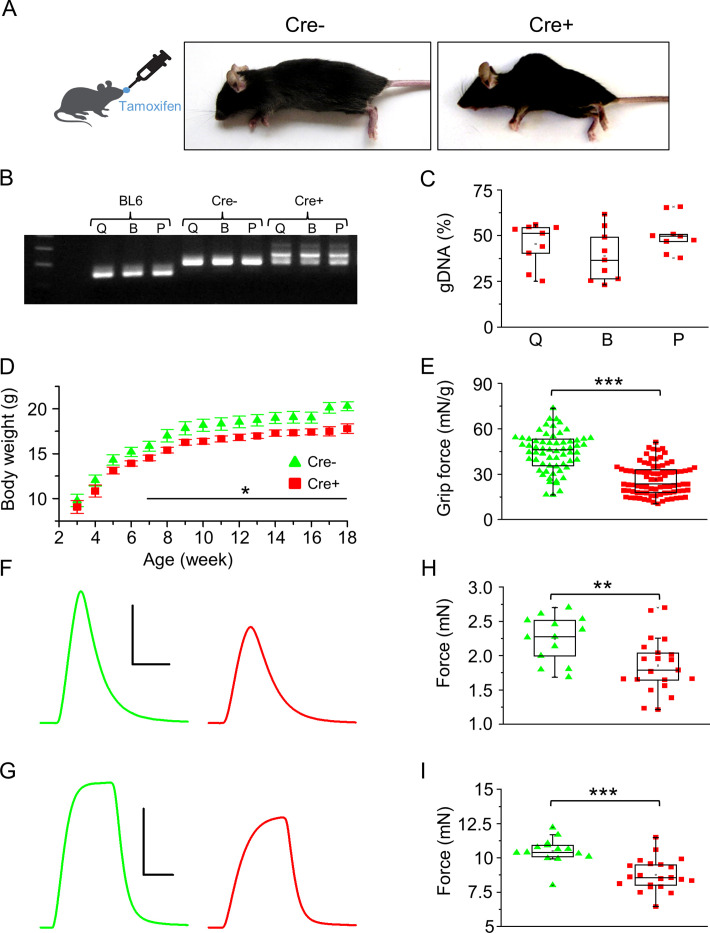
Figure 2. Skeletal muscle-specific knockdown of Septin7 resulted in a severe phenotype.
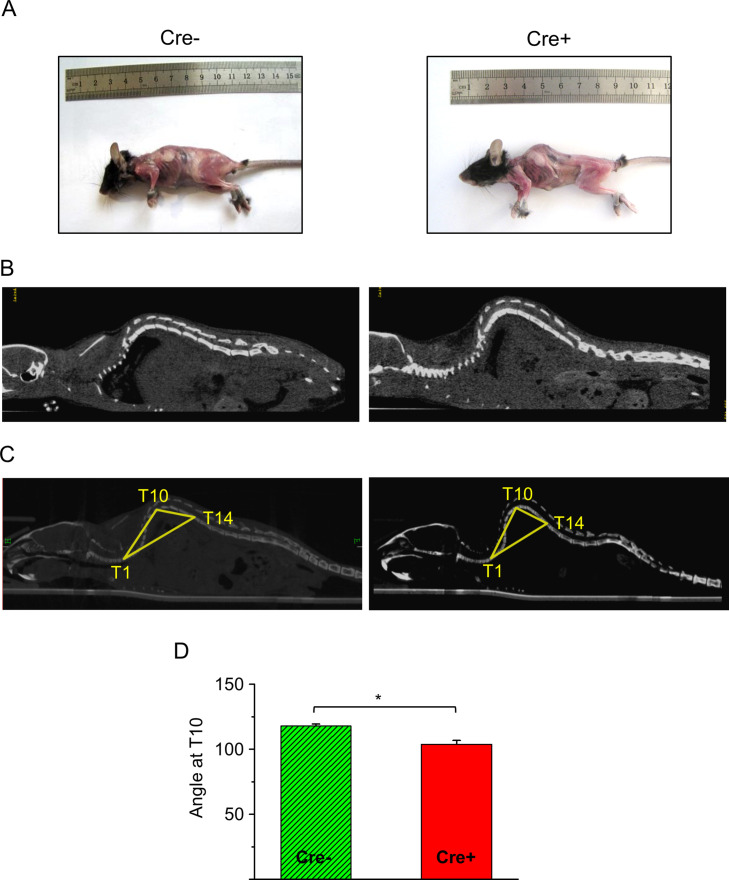
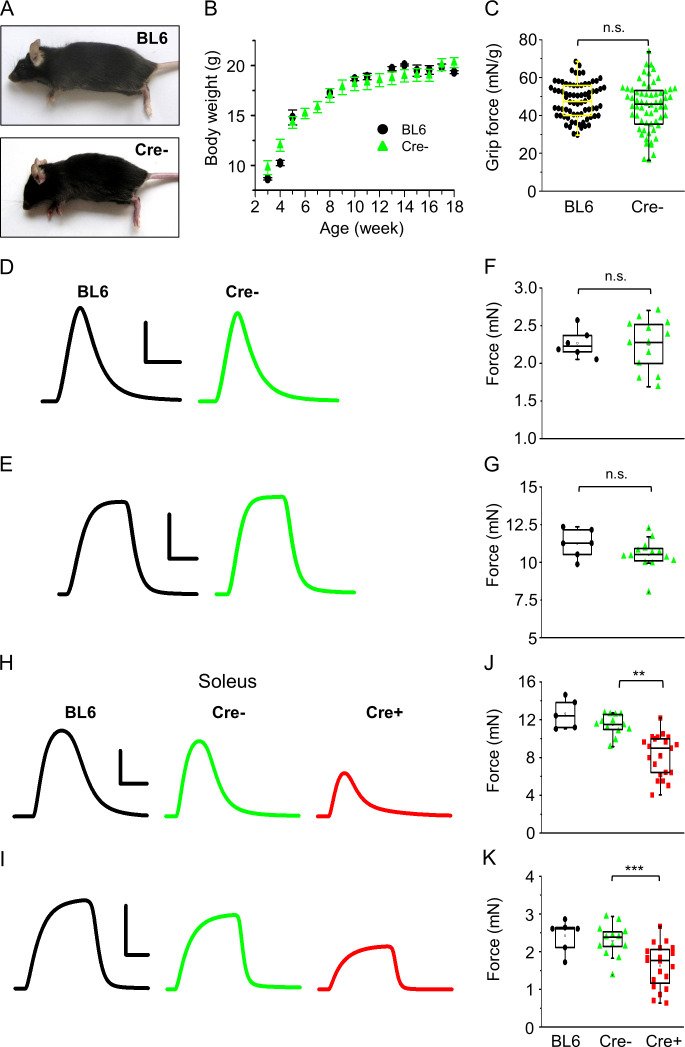
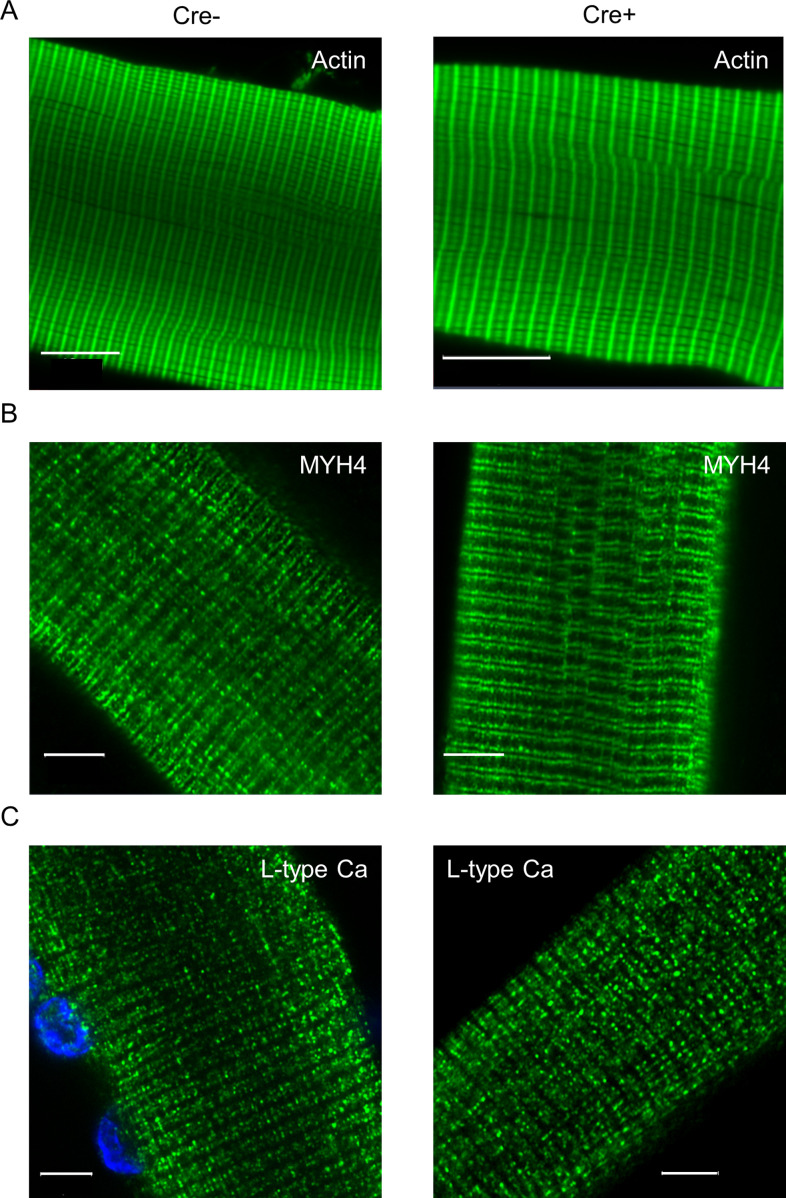
(A) Images of tamoxifen-fed Cre- and Cre+ mice (both Septin7flox/flox) at the age of 4 months (see Figure 2—figure supplement 1). (B) Three-primer PCR for detecting the partial deletion of the Septin7 gene in different skeletal muscle types of Cre+ mice (Q: m. quadriceps femoris; B: m. biceps femoris; P: m. pectoralis) and the lack of deletion in samples prepared from BL6 control and Cre- mice. In samples originated from Cre- animals, the floxed exon 4, while in wild-type tamoxifen-fed mice the unmodified exon 4 is demonstrated. First and last lines in the ladder correspond to 200 and 300 bp, respectively. (C) Pooled data of the percentage of exon 4 deletion in different muscle types of Cre+ mice. 14 littermates (nine Cre+ and five Cre-) were examined from three litters. Here and in all subsequent figures, the rectangles in the box plots present the median and the 25 and 75 percentile values, while the error bars point to 1 and 99%. (D) Changes of body weight in Cre- (green triangle, n = 11) and floxed Cre+ (red square, n = 14) mice. Black solid line shows where the difference is statistically different (p<0.05 from t-test). Error bars show SEM. (E) Grip force normalized to body weight in Cre- (n = 4) and Cre+ mice (n = 7). Representative twitch (F) and tetanic force (G) transients in m. extensor digitorum longus (EDL). Peak twitch (H) and tetanic force (I) in EDL from Cre- (n = 7) and Cre+ (n = 11) mice. Calibration in panel (F): 1 mN and 50 ms; (G): 5 mN and 100 ms. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 (from t-test). See also Figure 2—figure supplement 2. Main contractile proteins (actin and myosin) and L-type calcium channel distribution within single m. flexor digitorum brevis (FDB) myofibers isolated from Cre- and Cre+ animals were also investigated (see Figure 2—figure supplement 3).