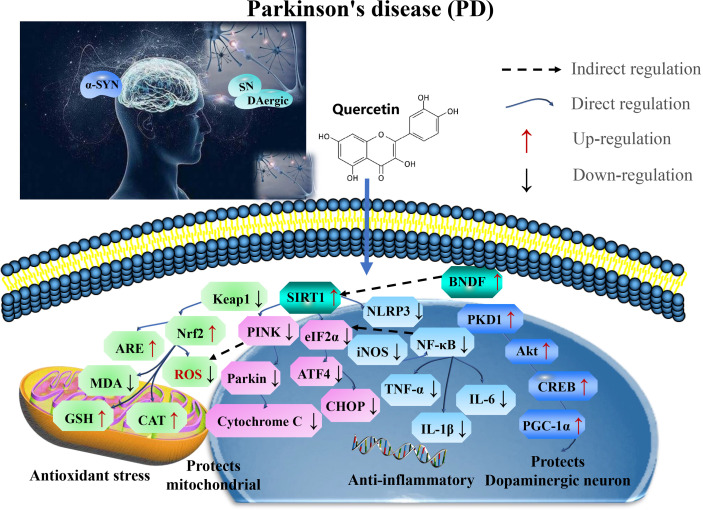
Figure 3.
Mechanisms of quercetin on attenuating Parkinson’s disease (PD). Quercetin is a potential therapeutic strategy for PD by targeting SIRT1. Developing therapies have shown that SIRT1/Nrf2/HO-1 mediated oxidative stress, SIRT1/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway ameliorates neuroinflammation SIRT1-mediated PKD1/CREB phosphorylation and BDNF gene expression, regulates mitochondrial disorders in dopaminergic neurons and SIRT1-PINK1-Parkin mediated mitochondrial autophagy in the astrocytes to maintain mitochondrial function. ROS, reactive oxygen species; 5-HT, 5-hydroxytryptamine; CAT, catalase; GSH-Px, glutathione peroxidase; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; NLRP3, NOD-like receptor protein 3; IL-1β, interleukin-1 β; CREB, cAMP response element binding protein; MDA, malondialdehyde; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; and GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein.