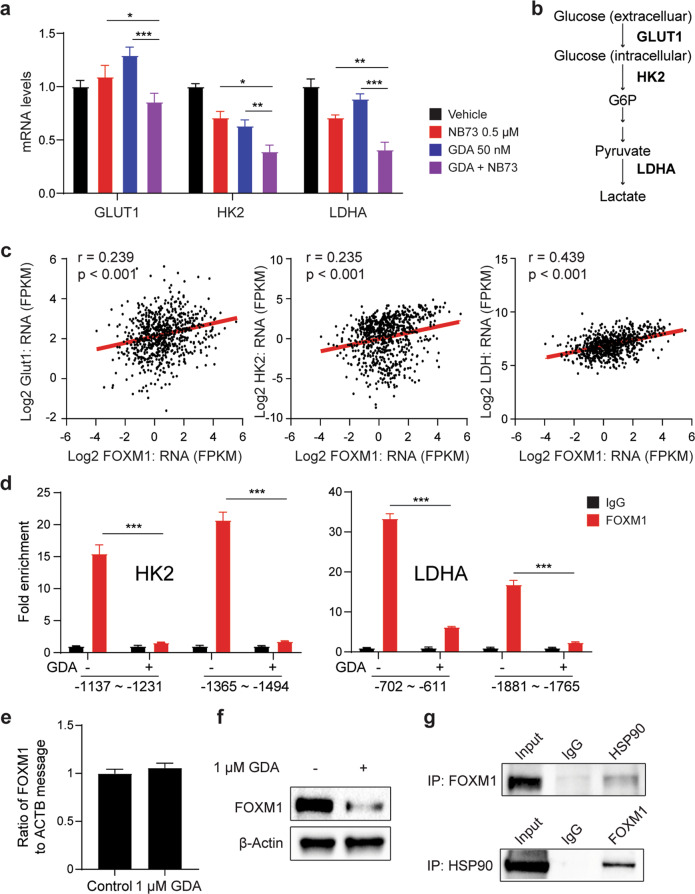
Fig. 7. GDA inhibits FOXM1-dependent expression of glycolytic genes.
a Message levels of 3 glycolytic genes in OPM2 cells exposed for 6 h to 0.5 µM NB73 (red), 50 nM GDA (blue) or both drugs (purple). Cells left untreated were included as control (black). Measurements relied on quantitative RT-PCR. b Position of genes from panel a in the metabolic pathway of glycolysis. GLUT1 is involved in glucose import. HK2 and LDHA catalyze the first and last step of glycolysis, respectively. c Gene expression scatterplots from the MMRF CoMMpass dataset used in Fig. 1. Pearson correlation coefficients are indicated. Linear regression lines have been highlighted in red using Adobe Illustrator. d ChIP-PCR analysis of FOXM1 binding to HK2 and LDHA promoter regions in OPM2 cells treated with 50 nM GDA (indicated by “+”) or left untreated (“–"). Size of PCR fragments and their location with respect to transcriptional start sites are indicated below the bar diagram. Fold enrichment of ChIP compared to baseline control was determined with the help of antibody to FOXM1 (red bars) and unrelated antibody of the same isotype (IgG, black bars), respectively. e RT-PCR analysis of FOXM1 mRNA levels in OPM2 cells treated with 1 μM GDA for 24 h or left untreated. f Western blot of FOXM1 from samples used in panel e. g Co-immunoprecipitation indicating physical interaction of FOXM1 and HSP90 in OPM2 cells. Immunoblots using specific antibodies to HSP90 (after IP using antibody to FOXM1) or FOXM1 (after IP using antibody to HSP90) are shown on top of each other. Isotype controls (labeled “IgG”) and whole-cell lysates not subjected to IP (labeled “input”) were included as controls. Considering that HSP90 interacts with approximately 400 client proteins, the mechanism by which GDA cooperates with NB73 is likely to go beyond the changes found here. In support of that, treatment of cancer cells using the HSP90 inhibitor, PF-4942847, suppressed FOXM1 by an indirect mechanism that involved upregulation of HSP70 [56].