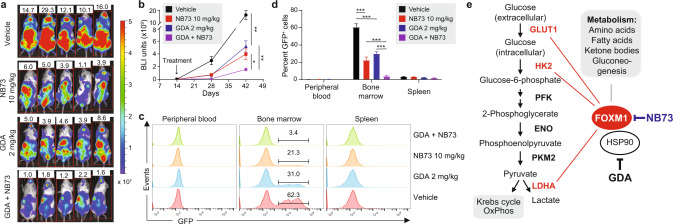
Fig. 8. Cotreatment with NB73 and GDA slows down myeloma in NSG mice.
a BLI images of NSG mice 42 days after tumor challenge (OPM2 cells). Mice were treated, beginning on day 14 after tumor challenge, with indicated drugs. Mice left untreated (top panel) were used as control. BLI intensity (indicated by colored bar to the right) ranged from 0.2–5 × 107 units. b Rate of tumor growth in mice from panel a based on quantitative BLI analysis on days 14, 28, and 42 after tumor cell transfer. Mice were treated using the indicated amounts of NB73 (red), GDA (blue) or both drugs (purple). Untreated controls are indicated in black. c Flow cytometric detection of GFP-labeled myeloma cells in mice from panel a. Cells of this sort were too rare to be enumerated in peripheral blood and spleen. The percentage of these cells in the bone marrow is indicated. d Statistical comparison of the abundance of GFP-positive myeloma cells in the bone marrow of mice from panel (a). e Working model on the role of FOXM1 in glycolytic energy production in myeloma. This study has shown that GLUT1, HK2 and LDHA are transcriptionally controlled by FOXM1 (indicated by thin red lines) and thus potentially targetable by FOXM1 inhibition for treatment of MM. Preclinical evidence gathered by other investigators has nominated PFK, ENO and PKM2 (bold black) as additional molecular targets for anti-glycolytic therapy of myeloma. This may be significant because activation of glycolysis promotes extra-medullary disease in patients with myeloma [57]. NB73, a small-molecule FOXM1 inhibitor, curbs glycolysis in myeloma. NB73’s efficacy can be enhanced by geldanamycin (GDA), an inhibitor of heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) that stabilizes FOXM1 in myeloma. Additional studies are warranted to elucidate the role of FOXM1 in oxidative phosphorylation (OxPhos) [58] and OxPhos-dependent pathways of drug sensitivity in myeloma [59], and to evaluate whether OxPhos inhibitors, such as "(IACS-010759) [60], under clinical development for cancer therapy [61] are effective in myeloma [62]. An important research task going forward is the mechanism with which FOXM1 impacts the metabolic pathways denoted in the gray text box on the upper right.