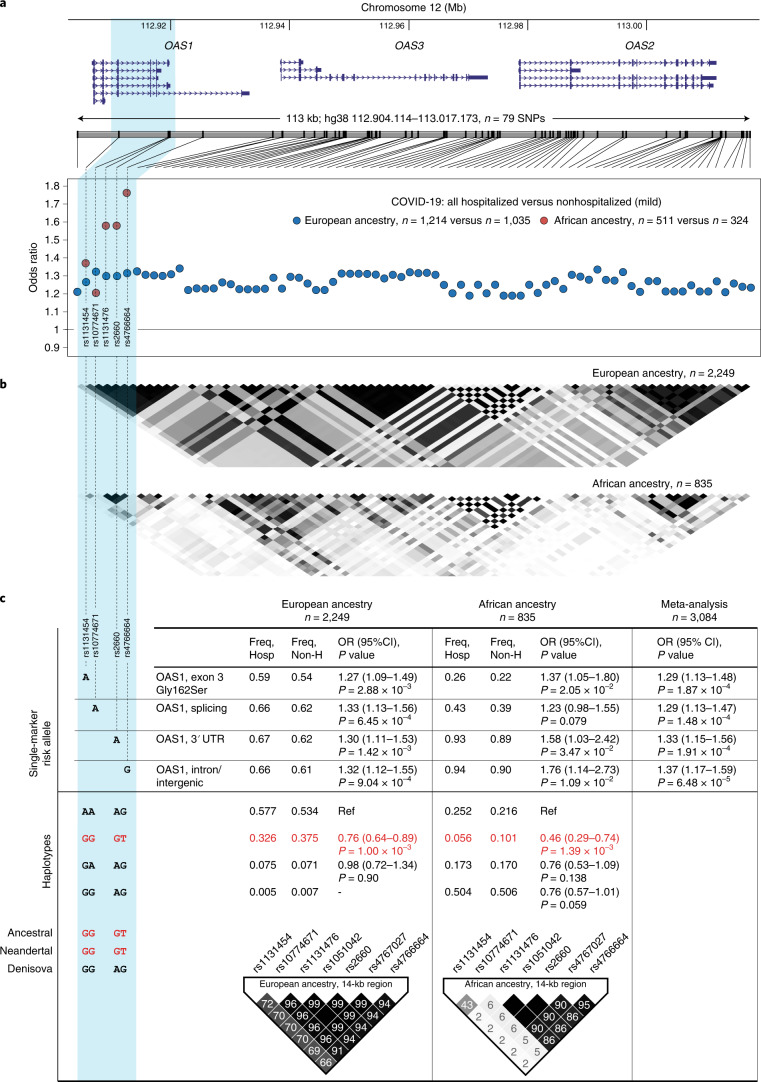
Fig. 1. Association analyses within the chr12q24.13 region for COVID-19 hospitalization in patients of European and African ancestries.
a, Genomic region and association results (ORs) for 79 genotyped or confidently imputed (r2 > 0.8) markers associated (logistic regression, P < 0.05) with hospitalized compared to nonhospitalized (mild) COVID-19 in patients of European (blue dots) or African (red dots) ancestries. The COVID-19 susceptibility GWAS lead SNP (rs10774671) is included, although it is not significantly associated in patients of African ancestry (P = 0.079). A blue highlight indicates the OAS1 region with markers significantly associated in both ancestries. b, LD (r2) plots of the region in COVID-19 patients of European and African ancestries. Darker shading in the plots indicates stronger correlations between markers. c, Single-marker and haplotype association analyses in patients with hospitalized compared to nonhospitalized COVID-19 performed with logistic regression and omnibus haplotype tests, respectively, controlling for sex, age, squared mean-centered age and 20 principal components. The GGGT haplotype comprised of ancestral alleles of the corresponding markers is shared with the Neandertal lineage of archaic humans and is protective from hospitalized COVID-19 in COVNET patients of European and African ancestries. Regional LD plots (r2, 14-kb region) are shown for the OAS1 region associated with protection from hospitalized COVID-19. Full association results for individual variants and haplotypes are provided in Supplementary Tables 1–4.