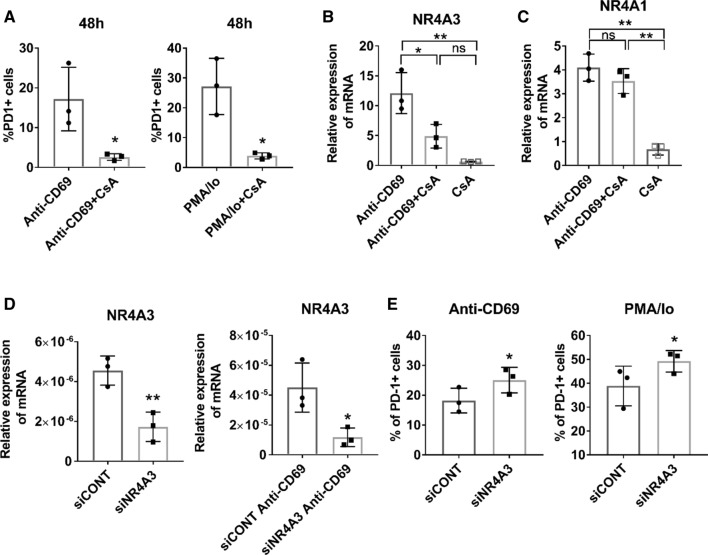
Fig. 3.
NFAT regulates PD-1 expression induced by CD69 engagement in T cells. A Cyclosporine A reduces the expression of PD-1 + in T cells. JKCD69 cells were incubated with crosslinked anti-CD69 with or without cyclosporine A (CsA), or phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate and ionomycin (PMA/Io) stimulated with or without CsA for 48 h. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3), and differences were determined by unpaired t test. * P < 0.05. B Cyclosporine A inhibits CD69-mediated NR4A3 induction. Relative expression of NR4A3 in JKCD69 incubated with anti-CD69 monoclonal antibody, with or without CsA and with CsA in resting cells for 4 h. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3), and differences were analysed with one-way ANOVA (Tukey post hoc test). * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01. C Induction of NR4A1 is independent of NFAT blockade. Relative expression of NR4A1 in JKCD69 with anti-CD69 antibody, with or without CsA and with CsA in resting cells incubated for 4 h. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3) and were analysed with one-way ANOVA (Tukey post hoc test). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. D Relative expression levels of NR4A3 mRNA after siRNA knockdown in resting and anti-CD69 stimulation conditions. Data showed are mean ± SD (n = 3), and differences were determined by unpaired t test. *P < 0.05. ** P<0.01. E siRNA interfering of NR4A3 expression enhances PD-1 + cell population. JKCD69 were stimulated with anti-CD69 or PMA/Io for 48 h. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3), and differences were determined by paired t test. *P < 0.05