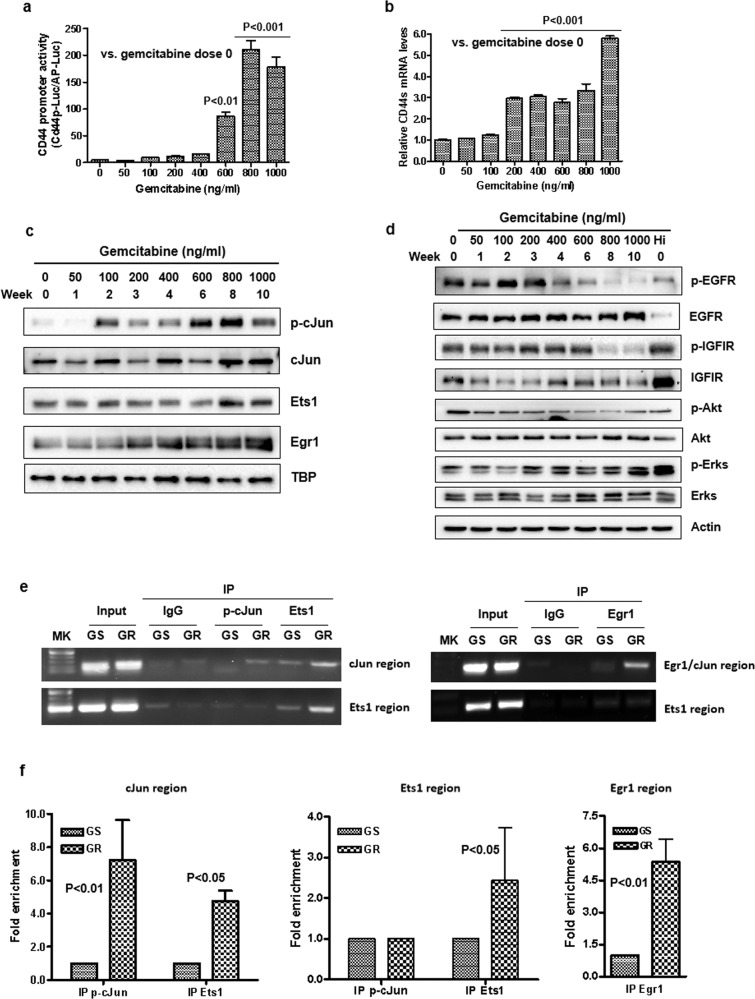
Fig. 3. Induction of CD44 transcription and increase in expression of cJun, Ets1, and Egr1 during the development of gemcitabine-resistant cancer cells.
a GS/CD44p-Luc cells were treated with elevated doses of gemcitabine weekly for up to 10 weeks. Conditioned media were collected for each treatment dose and assayed by a Secrete-Pair Dual Luminescence Assay Kit. The data were presented as mean ± SD in triplicate. P values were presented as compared to gemcitabine dose at 0 ng/ml. b Total RNA was isolated from cells as indicated in Fig. 1a and real-time RT-PCR was performed in triplicate for each dose using primers that only amplify CD44s. The relative CD44s expression was shown as mean ± SD. P values were presented as compared to gemcitabine dose at 0 ng/ml. c Nuclear proteins were isolated from the cells. The expression of transcriptional factors phosphor-cJun, cJun, Ets1, and Egr1 was detected by Western blot analysis. TBP was used as the loading control. d Western blot analysis of growth EGFR and IGF1R signaling in different dose stages of gemcitabine-treated cells. e, f Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays of binding of p-cJun, Ets1, and Egr1 to their regions of the CD44 promoter in GS and GR cells. e Samples were amplified by regular PCR, and the PCR products were run on 1.5% agarose gel. f Samples were analyzed by quantitative PCR. Fold enrichment is represented as signals obtained from immunoprecipitation with specific antibodies relative to signals obtained from immunoprecipitation with control IgG (mean ± SD from triplicate experiments).