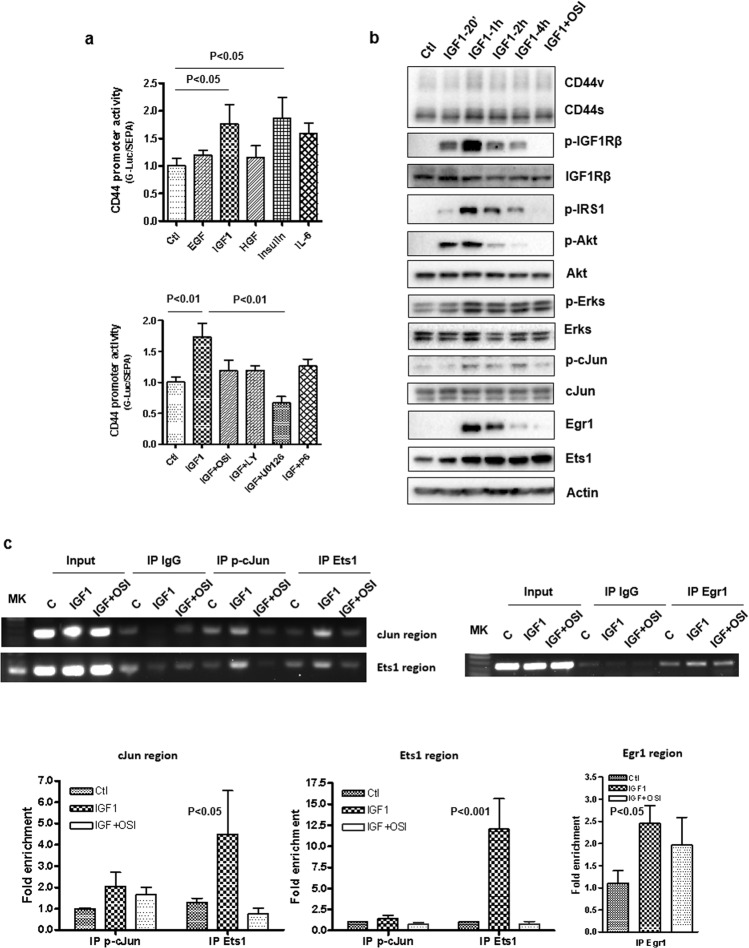
Fig. 5. IGF1 signaling induces CD44 promoter activity and enhances p-cJun, Ets1, and Egr-1 binding to CD44 promoter.
a 5 × 104/well of GS/CD44p-Luc cells were plated in a 24-well plate and serum-starved overnight. Cells were than treated with inhibitors OSI 906 (100 nM), LY 294002 (20 μM), U0126 (10 μM) or pyridone 6 (P6, 5 μM) for 2 h followed by adding growth factors: EGF (10 ng/ml), IGF1 (20 ng/ml), HGF (10 ng/ml), and Insulin (20 ng/ml) for 48 h. Conditioned media were collected and luciferase activities and alkaline phosphatase activities were measured using Secrete-Pair Dual Luminescence Assay Kit according to the protocol. Data were presented as mean ± SD from triplicate experiments. b GS cells were serum-starved overnight and stimulated with recombinant 20 ng/ml IGF1 for the period as indicated. For the IGF1 inhibitor sample, OSI906 was added 2 h before adding IGF1 and cell lysate was harvested at the one-hour point of IGF1 addition. Western blot analysis was performed with indicated antibodies. c GS cells were treated with 20 ng/ml IGF1 or IGF1 plus inhibitor OSI 906 (100 nM) for 24 h. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays with antibodies as indicated and normal IgG was used for non-specific binding control. Binding of p-cJun. ETs1 and Egr1 to CD44 promoter were shown in agarose gel with regular PCR products (upper panel) and quantitative PCR of ChIP samples (lower panel).