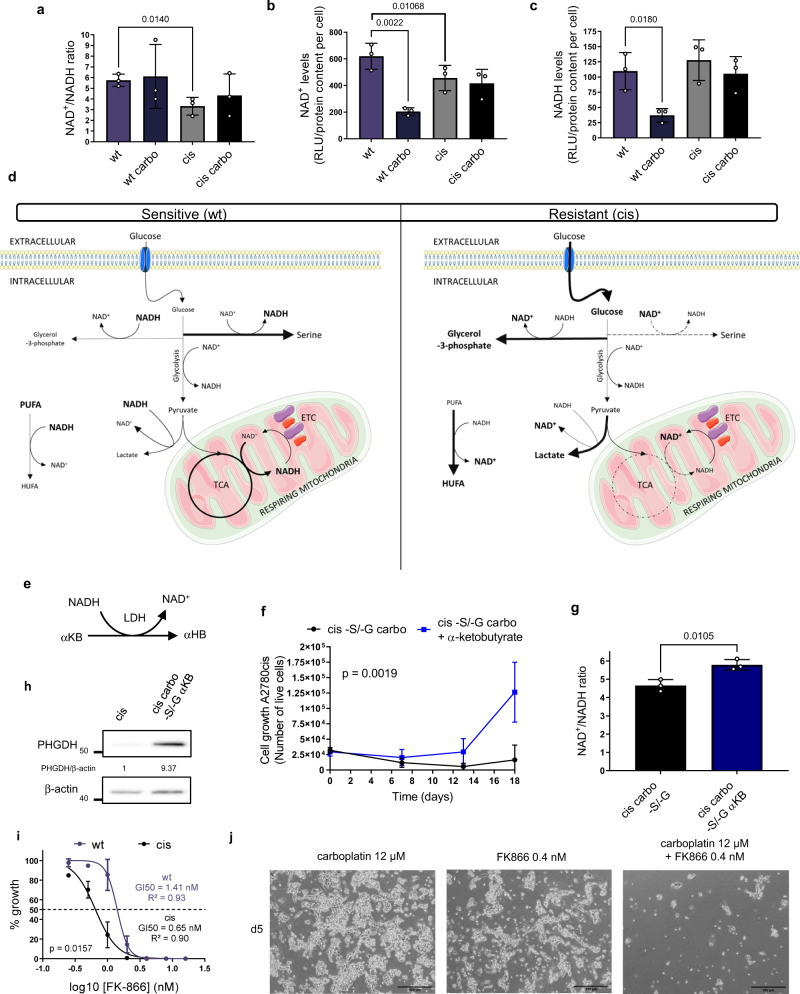
Fig. 5. Resistant cells rewire NAD+-regenerating pathways.
NAD+/NADH ratio (a), NAD+ levels b and NADH levels (c) determined by NAD+/NADH-Glo bioluminescent Promega assay, n = 3 biological replicates (with three technical replicates each time), unpaired two-tailed t-tests, data are represented as mean ± SD. d Metabolic map and observed alterations of wt vs. cis cells, more elaborate results in Supplementary Fig. 6. e The use of α-ketobutyrate (αKB) by lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) to generate α-hydroxybutyrate (αHB) and NAD+. f 2 mM αKB supplementation of serine/glycine starved cis cells with 6 µM carboplatin treatment, n = 3 biological replicates (with three technical replicates each time), repeated measures two-way ANOVA, data are represented as mean ± SD, p = 0.0019. g NAD+/NADH ratio of αKB supplemented serine/glycine starved cis cells with carbo treatment, n = 3 biological replicates (with three technical replicates each time), unpaired two-tailed t-test, data are represented as mean ± SD, p = 0.0105. h Representative western blot of PHGDH in αKB supplemented carboplatin treated ser/gly starved cis cells, n = 3 biological replicates. i GI50 of wt and cis cells to the NAMPT inhibitor Daporinad determined with trypan blue counting, n = 4 biological replicates (with three technical replicates each), unpaired two-tailed t-test between GI50 values, data are represented as mean ± SEM, p = 0.0157. j Representative images of cis cells under 12 µM carboplatin and 0.4 nM Daporinad treatment and its combination, scale bar is 500 µm, n = 3 biological replicates (with three technical replicates each). Some schematic art pieces in d were used and modified from Servier Medical Art. Servier Medical Art by Servier is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/). Source data are provided as a Source Data file. Carbo carboplatin treated, αKB α-ketobutyrate, αHB α-hydroxybutyrate, LDH lactate dehydrogenase, ETC electron transport chain, TCA trycarboxylic acid cycle, PUFA polyunsaturated fatty acids, HUFA highly unsaturated fatty acids.