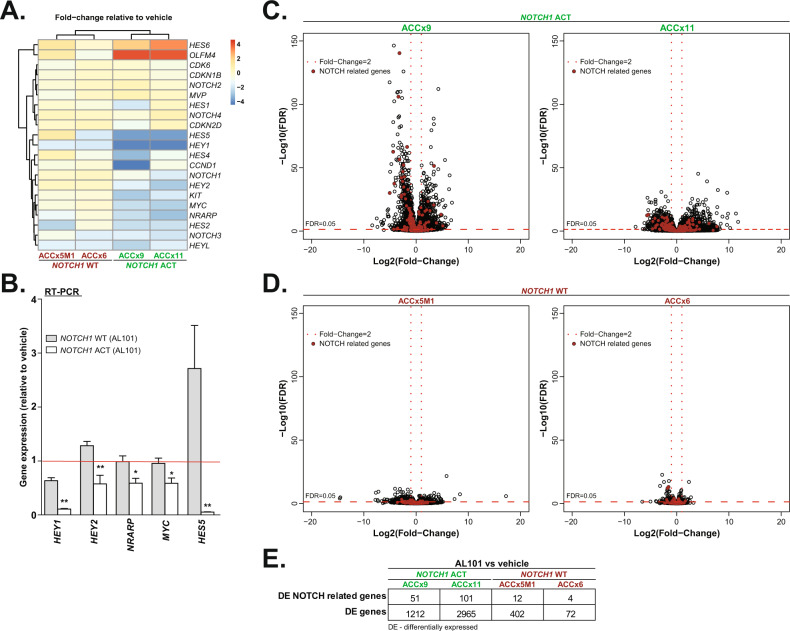
Fig. 5. AL101 inhibits NOTCH-mediated tumorigenic signaling in vivo.
A Fold-change in expression of 21 NOTCH-related genes (from normalized RNA-seq data) in animals treated with AL101 relative to vehicle-treated animals, displayed as a hierarchical clustering heatmap. Increased and reduced expression of genes is indicated with shades of red or blue cells, respectively. B Confirmation of RNA-seq data with RT-PCR analysis of selected NOTCH target genes in AL101-treated relative to vehicle-treated animals (red line). Gray bars: animals carrying wild-type NOTCH1 alleles; white bars: animals harboring NOTCH1 activating mutations. *p < 0.05, and ***p < 0.01. C, D Volcano plots depicting gene expression changes in AL101 versus vehicle-treated animals. The red circles represent genes included in a 478 NOTCH-related geneset curated from KEGG, PID, MSigDB, and PathwayCommons databases (see Supplementary Table 1 for details). E The table summarizes the total number of differentially expressed (DE) genes and NOTCH-related DE genes in AL101-treated animals relative to vehicle-treated counterparts.