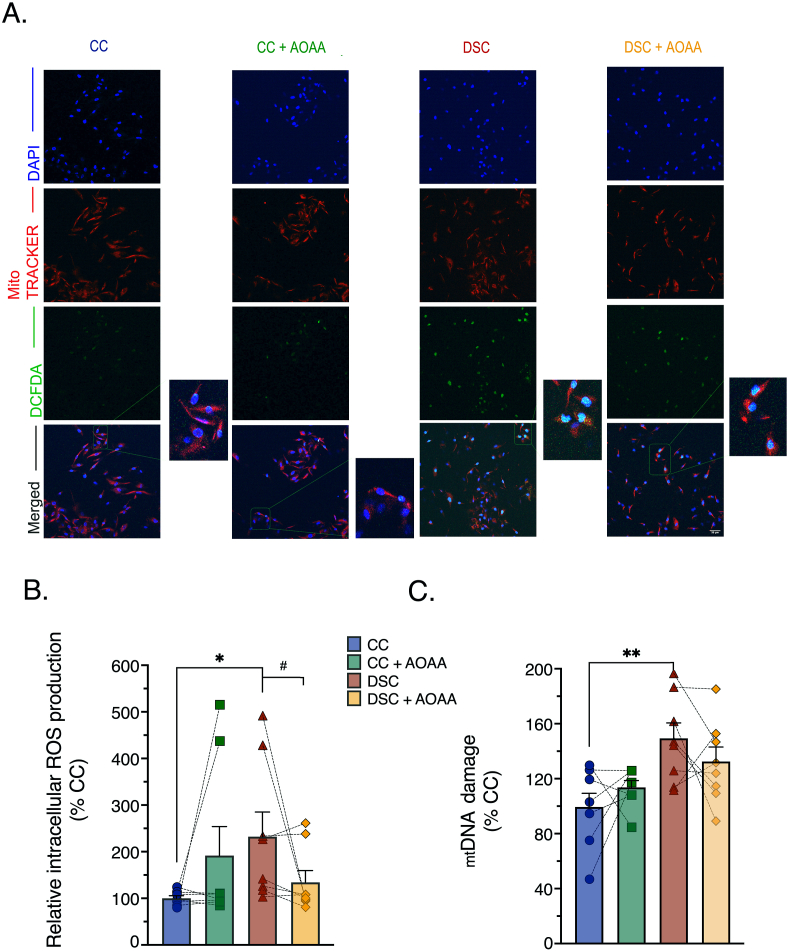
Fig. 4.
Pharmacological inhibition of CBS with AOAA attenuates the DS-associated overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and ameliorate mitochondrial DNA damage (mtDNA). (A): Representative pictures of control cells (CC) and dermal fibroblasts from individuals with Down syndrome (DSC) labeled with the redox-sensitive probe 2′,7’ –dichlorofluorescein diacetate (DCFDA) under basal (untreated) conditions and in the presence of AOAA treatment. (B): Quantitative analysis of the DCFDA fluorescent signal. (C): Assessment of mitochondrial DNA damage, expressed as a fold change to CC after baseline normalization to the corresponding mitochondrial copy number. Each bar graph represents the mean ± SEM of n = 8 human euploid control fibroblasts and n = 8 DS fibroblasts, as summarized in Table 1. Dotted connecting lines in the bar graphs indicate the same cell from a specific donor with/without AOAA treatment (3 μM, 24 h). *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01 indicate significant differences between DSC untreated vs. CC untreated; #p ≤ 0.05 indicates significant differences between DSC + AOAA vs. DSC untreated.