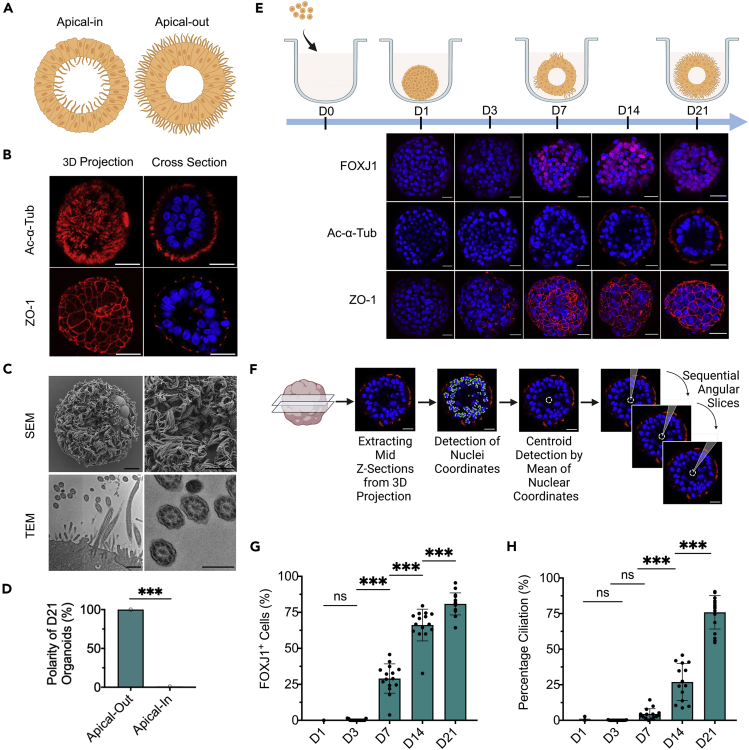
Figure 1.
Characterization of the engineered AOAOs
(A) Diagram of apical-in versus apical-out airway organoids.
(B) Immunofluorescence images of day 21 AOAOs stained with markers of cilia (Ac-α-Tub) and tight junction (ZO-1). Scale bar, 25 μm.
(C) SEM (scale bar, 10 μm) and TEM (scale bar, 800 nm (left), 400 nm (right)) images of AOAOs.
(D) Quantification of the percentage of day 21 (D21) organoids with apical-out versus apical-in epithelial polarity indicated by apical Ac-α-Tub localization.
(E) Time-series characterization of AOAO maturation by immunostaining of FOXJ1 (nuclear marker of ciliated cells), Ac-α-Tub, and ZO-1. Scale bar, 25 μm.
(F) Diagram showing the approach for assessing percentage ciliation by quantifying surface coverage of Ac-α-Tub expression.
(G and H) Time-series quantification of FOXJ1+ cell abundance (G) and percentage ciliation (H) in AOAOs. All data represent means ± SD from ≥15 organoids. ∗∗∗p < 0.001, Unpaired t-test/one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test.