Figure 2. LH GABAergic neurons are necessary to encode fear memories after reward learning.
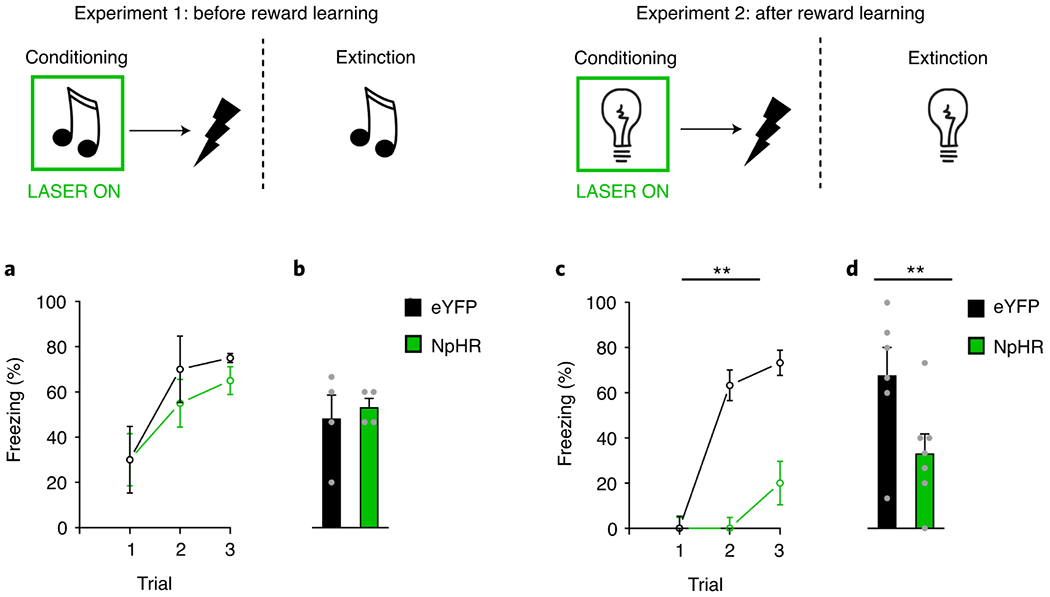
Responding is shown as mean level of freezing (%; ±SEM) Top: LH GABAergic neurons were inhibited by light (green rectangle) during the tone or light, and not during shock presentation, in both naïve rats (Exp 1; left) or a separate group of rats that had experienced reward learning (Exp 2; right). Bottom left: (A) shows freezing during conditioning in naïve rats, where inhibition of LH GABA neurons in the NpHR group (n=4 rats) had no impact on learning about fear relative to the eYFP control group (n=4 rats; trial: F2,12=5.812, p=0.017; trial x group: F2,12=0.187, p=0.831; group: F1,6=0.377, p=0.562). Similarly, (B) demonstrates that there were no differences in levels of freezing between groups during extinction (group: F1,6=0.206, p=0.666). Bottom right: (C) in a separate group of rats that had prior experience with rewards, inhibition of LH GABAergic neurons in our NpHR group (n=7 rats) significantly attenuated fear learning during conditioning relative to eYFP controls (n=6 rats; trial: F2,22=17.886, p=0.000; trial x group: F2,22=9.133, p=0.001; group: F1,11=29.615, p=0.000). (D) shows this difference was maintained in an extinction test with LH GABA neurons intact (group: F1,11=5.553, p=0.038). Data were analyzed with a repeated-measures ANOVA, which utilize a two-sided test.
