Figure 1:
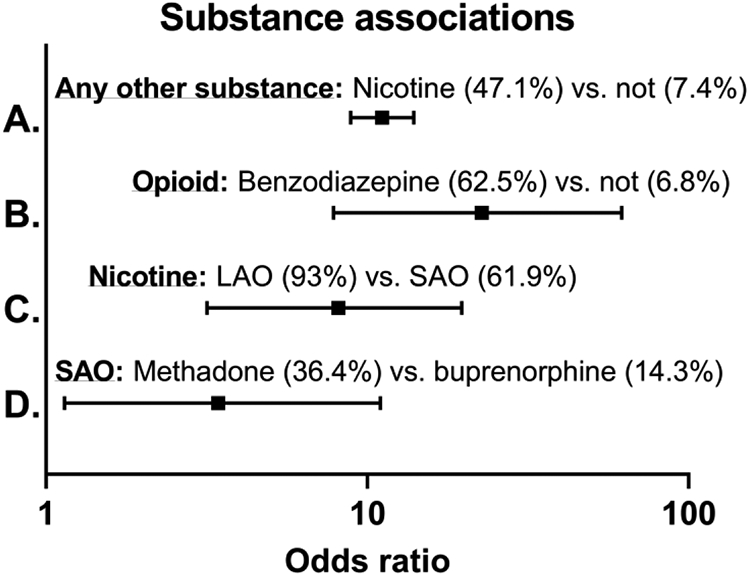
Odds ratios depicting for A.) The 11.1 times increased odds of testing positive for another substance if a mother tests positive for nicotine. B.) 22.7 times increased odds of testing positive for an opioid if a mother tests positive for a benzodiazepine C.) 8.1 times increased odds of testing positive for nicotine if a mother tests positive for a long-acting opioid (LAO) compared to a short-acting opioid (SAO) and D.) 3.4 times increased odds of testing positive for a SAO if a mother tests positive for methadone compared to buprenorphine.
