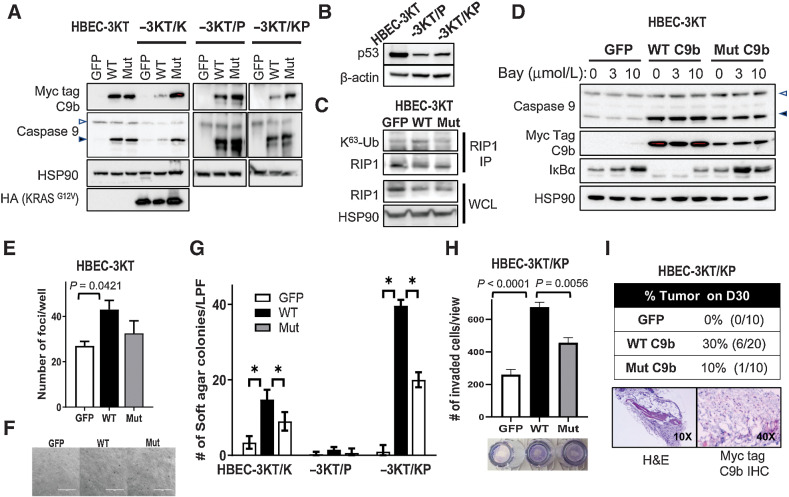
Figure 1.
C9b activates NF-κB in HBEC-3KT cells and cooperates with KRAS activation and p53 loss driving AIG and invasion in vitro and tumor growth in vivo. A–D, Western blot analyses with indicated antibodies of HBEC-3KT, -3KT/K (KRASG12V), -3KT/P (shTP53), and -3KT/KP cells expressing GFP, WT, or AT/GG mutant (Mut) C9b (with a Myc-tag). C, RIP1 immunoprecipitation (IP) followed by immunoblotting with K63-Ub antibody shows increased RIP1 K63-Ub by WT C9b in HBEC-3KT cells (in growth supplement free media). In D, HBEC-3KT cells were treated with 0, 3, 10 μmol/L Bay 11–7082 for 15 hours. WCL, whole-cell lysates. The empty and filled triangles denote C9a and C9b proteins, respectively. E, Clonogenic assays of parental HBEC-3KT cells expressing GFP, WT, or Mut C9b. The graph shows numbers of clonal foci per well on D10. F, Bright field images (10x) of HBEC-3KT cells expressing GFP, WT, or Mut C9b grown in soft agar on D45. G, Number of colonies per low power field (LPF) view grown in soft agar on D45 (*, P ≤ 0.0002). H, Number of invaded HBEC-3KT/KP cells expressing GFP, WT, or Mut C9b through Matrigel at 22 hours per LPF view. I, SCID Tumor take rate of HBEC-3KT/KP cells expressing GFP, WT, or Mut C9b on day 30 postimplantation (top) and H&E, Myc-tag, and c-Myc IHC images (bottom). Data are means ± SD; n = 3 each. Adjusted P values are determined by ANOVA Tukey multiple comparison test.