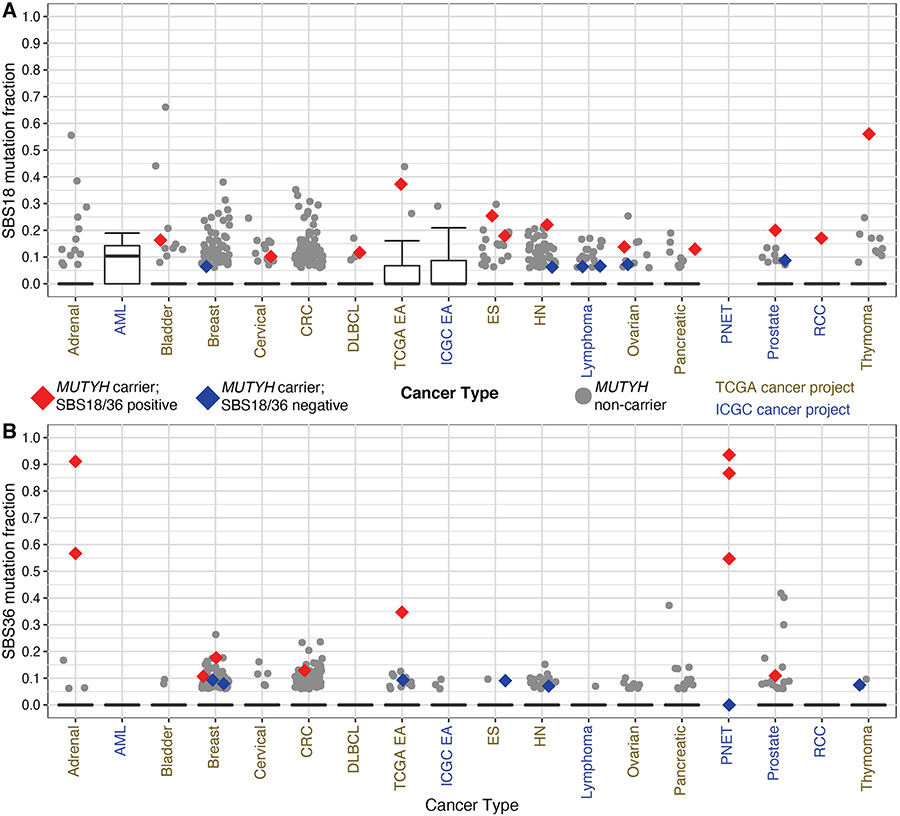
Figure 2: Single Base Substitution Signature 18/36 fractions Across TCGA and ICGC.
Distribution of Single Base Substitution Signature 36 (SBS36) (A) and SBS 18 (B) by genomic project and cancer type. Tumor types displayed possessed at least one MUTYH carrier with a detectable mutation signature 18 or 36. Red markings designate samples from MUTYH carriers that had detectable components greater than 0.10 and in the top quartile in their respective tumor type (SBS18/36 positive). Blue markings designate those samples from carriers that failed to achieve a minimum component of 0.10 (SBS18/36 negative), but with a detectable fraction. TCGA-ESCA project was subdivided into esophageal adenocarcinoma (EA) and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ES). The TCGA-COAD and TCGA-READ projects were combined into colorectal cancer (CRC), and the ICGC PRAD-CA and PRAD-UK were combined into prostate cancer. Four pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNETs) from MUTYH carriers were plotted irrespective of fractions given known association with MUTYH-associated signatures. HN = Head and Neck squamous cell carcinoma, AML = acute myeloid leukemia, RCC = renal cell carcinoma.