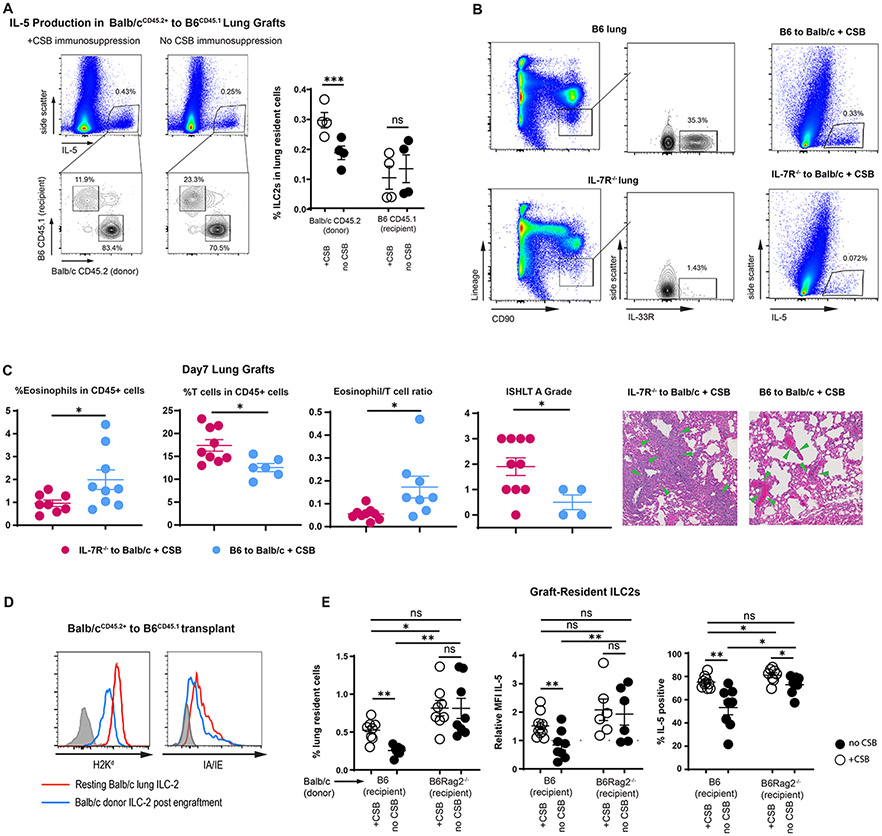
Alteration of Graft-Resident ILC-2.
(A) Relative donor vs. recipient IL-5-producing cells in the presence or absence of CSB immunosuppression. Left panels demonstrate all IL-5-producing cells and the right panel is gated on CD90+Lin−ST2+ ILC2s as a percent of all lung cells. (B) ILC2 levels in B6 IL7R−/− vs. wildtype (left panel); IL-5 production in lung grafts of B6 to Balb/c + CSB vs. B6 IL7R−/− to Balb/c + CSB (right panel). (C) Relative abundance of eosinophils and T cells, eosinophil/T cell ratio and ISHLT A grade of B6 IL-7R−/− vs. B6 wildtype lungs implanted into Balb/c recipients in the presence of CSB immunosuppression. Green arrows indicate perivascular lymphocytic infiltration. (D) MHC Class I and II expression in tissue-resident ILC2s of both resting and Balb/c lungs after transplantation into B6 mice. ILC2s identified as CD90+Lin−ST2+ CD45.2+CD45.1− cells in Balb/cCD45.2+ to B6CD45.1+ graft recipients. (E) Relative numbers as well as IL-5 expression, defined as relative MFI and % positive, of graft-resident ILC2s in the presence or absence of CSB immunosuppression in Balb/c to B6 wildtype vs. B6 Rag2−/− mice. Tissue was collected and analyzed on post-engraftment day 7 for (B)(C) and on day 4 for (A)(D)(E). CSB=co-stimulatory blockade; MFI = Mean fluorescent intensity (geometric mean). ns=p>0.05; * =p<0.05; **=p<.01; ***=p<.001