Fig. 2. First-stage analysis: Baseline cross-sectional association of BALs with PA, linear model adjusted for age, sex, race/ethnicity, LDL-C, total-C, and smoking.
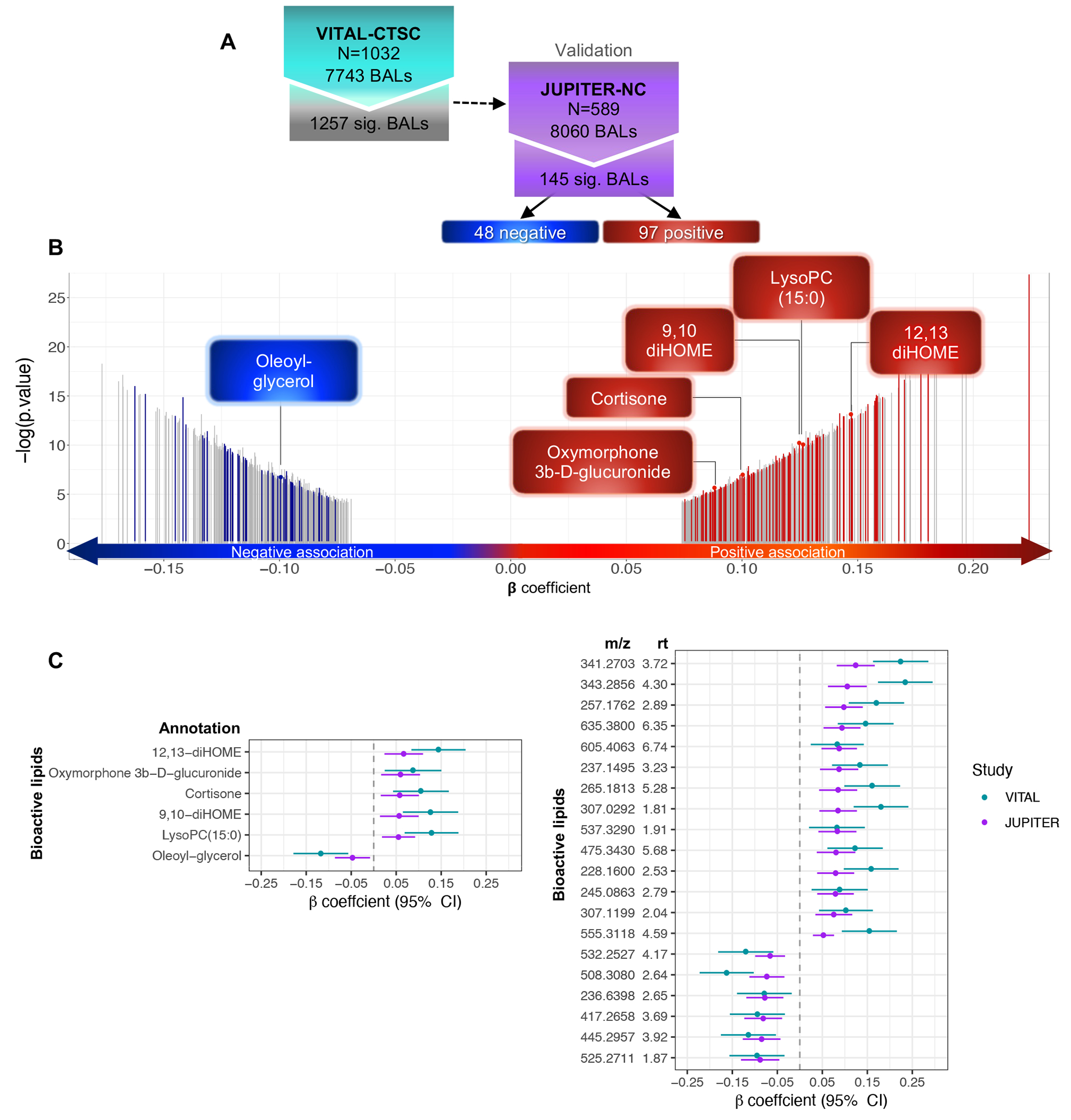
A) Flowchart of PA-BAL associations in VITAL-CTSC with validation in JUPITER-NC; B) Distribution of 1,257 BALs associated with baseline PA in VITAL-CTSC (FDR < 0.1), according to β-coefficients for SD change in BAL per exercise SD=21.8 MET-hrs/wk. Of those, 145 BALs validated in JUPITER-NC (FDR < 0.1 and the same directionality). Negative (blue) and positive associations (red) are highlighted, and gray bars represent significant BALs in VITAL-CTSC not validated in JUPITER-NC. Annotations are indicated. C) PA-BAL significant associations (FDR < 0.1) in both VITAL-CTSC and JUPITER-NC. Symbols with error bars are β -coefficients per SD of PA in VITAL-CTSC (blue) or per category in JUPITER-NC (purple), with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Annotated BALs are presented, as well as the top 20 novel BAL (ranked based on unadjusted P-values in the validation cohort). Abbreviations: m/z – mass to charge ratio; rt – retention time.
