Fig. 1.
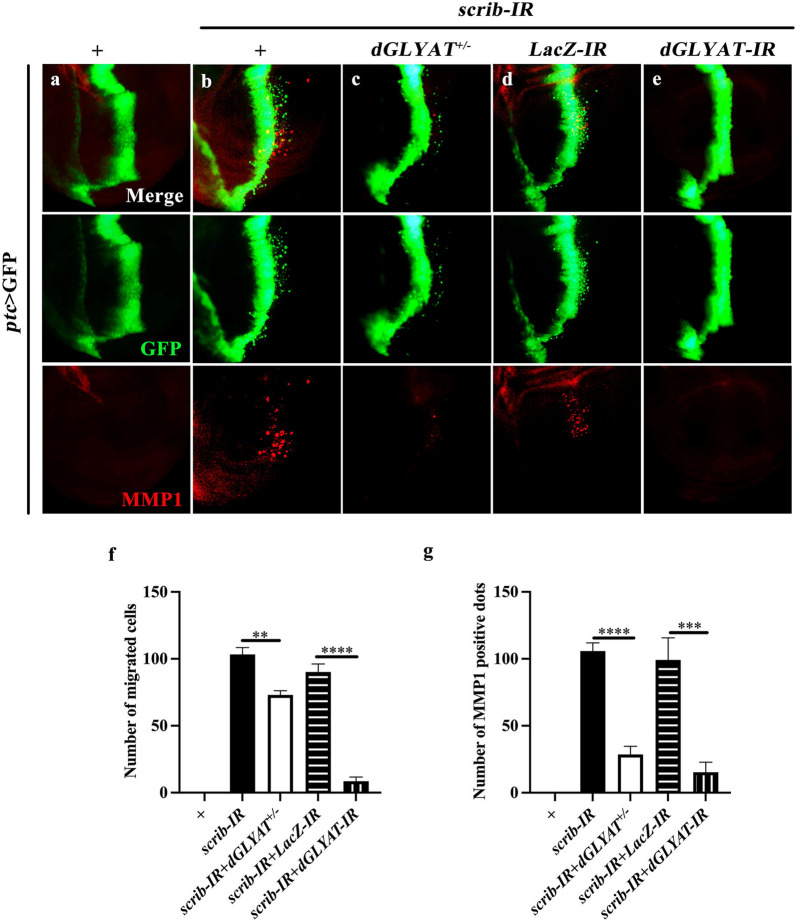
dGLYAT is required for cell polarity disruption-induced cell invasion. Fluorescent micrographs of Drosophila third instar larval wing discs are shown (a-e). Compared with the ptc > GFP control (a), ptc > scrib-IR induced cell migration from A/P boundary toward posterior and elevated MMP1 expression (b). Both phenotypes were significantly suppressed by heterozygous mutation (c) or RNAi expression of dGLYAT (e). LacZ RNAi served as a negative control (d). f Statistic of number of migrated cells is shown (left to right: n = 10, n = 8, n = 5. n = 8, n = 10). g Statistic of number of MMP1 positive dots is shown (left to right: n = 10, n = 12, n = 5. n = 5, n = 10). t-test was used to compute P-values. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. Detailed genotypes: a ptc-Gal4 UAS-GFP/+, b ptc-Gal4 UAS-GFP UAS-scrib-IR/+, c ptc-Gal4 UAS-GFP UAS-scrib-IR/dGLYATc02982, d ptc-Gal4 UAS-GFP UAS-scrib-IR/+; UAS-LacZ-IR/+, e ptc-Gal4 UAS-GFP UAS-scrib-IR/+; UAS-dGLYAT-IR/+